Although urban areas occupy less than 1% of the world’s land surface, they contribute over 90% of the global economy. By 2014, already 50% of the world’s population was living in urban areas, and this figure is increasing (United Nations, 2015). Urban impervious surfaces, such as buildings, parking lots and transportation networks, have been widely recognized as an important indicator of urban expansion and its related environmental issues, such as public health, urban heat islands and various environmental pollutants. In the long run, and especially for areas that are subject to a very strong urbanization process, such as the Pearl River Delta (PRD), a comprehensive assessment of impervious surfaces dynamics will be vital and urgent in the assessment and management of these effects. Unfortunately, it has been increasingly difficult to accurately assess the urban impervious surfaces in this area because of its wide geographical extent. PRD has witnessed the world’s most dramatic urbanization process since 1980s, thanks to the implementation of the reform and opening up policies of the Chinese Government. More specifically, PRD is a special metropolitan area and includes three different urban planning and development policy bodies, Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau. The increase of urban impervious surfaces in PRD has led to a wide range of environmental issues such as urban flooding and air and water pollution. These effects have been threatening the environmental equilibrium and human health in the whole PRD region. Therefore, a continuous and timely monitoring of the dynamics of impervious surfaces in PRD using remote sensing has been identified by both local and central governments. However, PRD is located in a subtropical climate zone characterized by rainy and cloudy weather throughout the year, and thus requires the most advanced remote sensing technology to overcome weather-related difficulties. The ultimate objectives of this research are to: 1) estimate and validate the urban impervious surfaces extents by manifold learning and deep learning jointly considering optical and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite data; and 2) investigate and model the inter- and intra-annual dynamics of the urban impervious surfaces in PRD exploiting available time-series data analysis techniques. The outcomes of the research will: 1) include a novel methodological framework for the use of manifold learning and deep learning for accurate impervious surface estimation from optical and SAR data; and 2) provide a comprehensive understanding of the inter- and intra-annual dynamics of the urbanization in the PRD region.
With so many typhoon passages each year, the Hong Kong coastal area is strongly influenced by extremely strong wind events during the typhoon season. The typhoon related storm surges can induce disastrous inundations in the Hong Kong coastal area, resulting in serious casualty and property loss. Thus, rapid and precise prediction of the storm surge-induced inundations is of great importance to mitigation of inundation disasters in the coastal area of Hong Kong. Because of the complexity in Hong Kong coastal topography and elevation and the complicated interaction between storm-generated strong ocean currents and the coastal elevation, however, there has been no effective inundation prediction system that could be applied to the Hong Kong coastal area.
This project aims at developing a precise and fine prediction system for storm surge inundation in the Hong Kong coastal area with the satellite remote sensing technology on the platform of open source geographic information system (GIS), incorporating the enhanced Hong Kong coastal digital elevation model (DEM) database to provide an operational inundation forecast system for relevant users. The system will play an importance role in Hong Kong oceanic disaster mitigations.
Mangrove forests are ecosystems of considerable ecological, biological and socioeconomic significance as: 1) vital habitats for a wide variety of animal and plants species, 2) important sources of carbon for detritus-based food webs in adjacent coastal waters, 3) a means of reducing the erosion of shorelines, and 4) buffers against the impact of storm waves and floods. However, mangrove forests have been significantly eroded over the past century due to various human activities such as agriculture conversion, urbanization and tourism. Hong Kong benefits from a number of mangrove forests which continue to play important ecological and socioeconomic roles to local communities. Unfortunately, mangrove forests cover has rapidly decreased in the past few decades due to increasing agricultural exploitation and infrastructural development such as new highways and airport as well as associated construction. Given the importance of mangrove forests, timely and accurately monitoring at large scale is imperative for their conservation and restoration. Mangrove forests are usually located in inaccessible regions and often temporarily inundated, which makes it difficult to carry out large-scale and long-term monitoring with traditional field survey approaches. Therefore, satellite techniques have been widely employed for large scale monitoring. However, the coarse spatial and spectral resolution of early satellite imaging restricted the detail and accuracy of the results. With the latest high resolution satellite sensors, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data has been increasingly reported to be sensitive to biomass and structural attributes of vegetation and thus holds great potentials for mangroves monitoring. Nevertheless, the potentials of SAR for discriminating mangrove species are still underexplored, especially with fully polarimetric SAR data. The general aims of this research are to: 1) investigate the comprehensive potentials of multi-frequency polarimetric SAR data with single, dual, compact and full polarizations for improving the discrimination of mangrove species in Hong Kong, and 2) develop effective and efficient methods for synergizing polarimetric SAR data and high resolution optical data at both feature and decision levels. The outcomes of this proposed research will not only include a comprehensive method for investigating a diversity of polarimetric features by evaluating their effectiveness and responses to various mangrove species, but also a general framework for incorporating high resolution optical and multi-frequency polarimetric SAR features for mangrove species discrimination. The implementation of this project can serve as a general model to promote polarimetric SAR techniques for mangrove forests monitoring, and finally, to support the conservation and restoration of mangrove forests.
Impervious surfaces (IS), as the major land surface modification of rapid urbanization in many metropolitans in the past decades, have been widely recognized as imperative indicator for not only urban environmental issues (e.g. water quality, aerosols, urban heat island and climate change) but also socio-economic issues (e.g. population distribution and urban planning) from local, regional to global scales. Pearl River Delta (PRD) is such a typical metropolitan with large area of IS, which have been leading to various environmental and socio-economic problems, and thus urgently require accurate estimation of IS for timely monitoring and understanding its urbanization processes. Given its importance, numerous methods have been developed for IS estimation (ISE) from satellite data. However, most of them were tested in temperate continental areas and with only optical satellite data. Only a few of them considered the case in subtropical humid areas like PRD, where climatology (e.g. rainy and cloudy) and phenology are special and different from temperate regions and thus cause great difficulties for remote sensing studies. To overcome the difficulties, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data has been synergized with optical data in subtropical regions in the past several years, but only single polarization SAR data were employed and the accuracy is far from satisfactory. Multi-polarimetric SAR data have been frequently reported to be able to provide much richer information in urban areas, while its potential application in ISE is still underexplored and many challenging problems remain unaddressed. The general aims of this research are to: 1) Investigate the full potential of multi-polarimetric SAR data, including dual, compact and fully polarimetric SAR data, for improving ISE in subtropical urban areas; and 2) Develop effective fusion methodology for synergizing optical and polarimetric SAR data at both feature and decision levels from city to metropolitan scales. The outcomes of this proposed research will not only provide a comprehensive feature extraction framework for polarimetric SAR data, but also evaluate the effectiveness of these polarimetric SAR features by their contributions to ISE at both feature and decision levels. Additionally, as a validation of the proposed methodology, PRD will be employed for case studies from city scale and metropolitan scale. The implementation of this project can serve as a general model to promote the applications of optical and polarimetric SAR data in accurate ISE of other humid subtropical urban areas in the world.
Mangroves are an assemblage of woody hydrophytes that are foundational species of the dense inter-tidal forest ecosystems that occur along tropical and sub-tropical coastlines, estuaries, lagoons, and rivers. Mangrove forests sustain productive, biologically unique, and economically important ecosystems. In Hong Kong, the value of mangrove forest has not been fully appreciated until the latest two decades. In 1998, Mai Po and Inner Deep Bay were listed under the Ramsar Convention as a Wetland of International Importance, constituting the first Ramsar Site Strategy and Management Plan (RSMP) in Hong Kong. This research aims to comprehensively exploit the textural information embedded in the very high resolution satellite data, with respect to their contributions to discriminating various mangrove species. The relationship between this sophisticated textural information and mangrove species, regarding their stand characteristics (e.g. leave, trunk, tree height and biomass), will be explored and evaluated. The outcome of this study will be able to improve the accuracy of mangrove species discrimination and thus support the conservation and restoration of mangrove forests in Hong Kong.
Hong Kong is sensitive to variability in mean sea level (MSL) and ocean tides due to El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events at yearly scales, and due to monsoons at seasonal scales. Hong Kong’s MSL rate is irregular over the past 40 years, and the area is subject to land subsidence. The combined effect of MSL rise and tidal amplitude change amplifies inundation risks, and is further amplified by upper-ocean warming in the past 20 years. The El Nino event of 2015-2016 is on track to match the intensity of the 1997-1998 and the 1982-1983 events.
The objectives of this study are to quantify ENSO and seasonality effects on MSL and ocean tides in Hong Kong at yearly and monthly time scales, and to determine the future of water levels in the region under future ENSOs for concerns such as coastal planning and shipping. The objectives will be achieved through assimilation and harmonic analysis of historical tide gauge data, satellite data, and climate reanalysis data. Yearly analyzed data will be used to quantify tidal variability during historical and currents ENSO events, to be compared to non-ENSO years. Monthly analyzed data will be utilized to quantify monsoon-induced seasonality by comparing months of strong monsoon to that of weak monsoon. A barotropic ocean model will be employed to explore mechanisms contributing to observed tidal changes.
This study will help to understand the water level change dynamics that is critical to effective coastal urban planning, changes to local ecosystems in Hong Kong.
The geographic location of Hong Kong specifies that the marine environment has significant impacts on economics and society of Hong Kong, and coastal marine hazards and pollution greatly threaten its living and ecological environment. The project aims at establishing a satellite remote sense-based system for monitoring Hong Kong marine dynamic environments. The project will focus on developing new highly precise satellite data algorithms and software for retrieval of accurate ocean dynamic parameters. Hong Kong Real-time monitoring data from the system will improve accuracy of marine environmental forecast for Hong Kong coastal waters, assist the marine ecological environment protection and disaster mitigation, and help to build up a sustainable marine environment for the Hong Kong coastal water.
The Ocean is an important factor that affects thermal and dynamic structures of atmosphere. Because of lack of observation data, little has been known about the influence of the ocean meso-scale temperature fronts on the regional atmospheric circulation and climate variability. Development of the satellite remote sensing technology provides us high resolution data of sea surface temperature and surface wind fields. Based on the remote sensing data, it was found that the Kuroshio temperature front may generate an atmospheric convergence that appears in entire troposphere. However, till now, it is still unclear about the generation mechanism and fine structure of the atmospheric convergence. Thus, related topics is raised in the proposal aiming at clarifying generation mechanism of the atmospheric convergence and its impacts on the regional, atmospheric circulation and the regional climate through analysis on the remote sensing and reanalysis data and the numerical simulations. The study will help to better understand the process and mechanism of influence of the Kuroshio warm current on the East Asian climate, clarify the detailed dynamic and thermal structures, and improve the prediction of the regional atmospheric circulation.
The discharge of the Pearl River forms a buoyant plume in coastal waters, which is transported eastward from the river mouth and occupies Hong Kong near- and offshore waters, driven by southwesterly winds in summer wet, high-flow season. The river discharge carries inland nutrients and micro-elements into the coastal water area, facilitates a rich primary production area in the Pearl River plume region. Pearl River delta holds one of the densest populations in the world and plays an important role in China rapid development in economy and society.
However, with the rapid economic growth in the river delta and upstream regions, more and more inorganic and organic materials including various kinds of sediments, industrious wasters and sewage are poured into the river, the river water is heavily polluted, and its water quality is getting more and more deteriorated, which greatly threatens ecological environments of the Hong Kong coastal waters). The water equality or bio-physical characteristics of the Pearl River plume are mainly controlled by its dynamic properties such as plume circulations, frontal processes, mixing characteristics. The complex ecosystem in the Hong Kong coastal water cannot be fully unveiled without deep understanding of the plume dynamics. The strongly baroclinic plume can significantly affect the regional ocean circulation. Therefore, investigations of the Pearl River plume dynamics are of great importance for understanding ecological environments and improving numerical simulation and forecast in Hong Kong coastal waters. However, the physical processes of the Pearl River plume have been poorly understood because of insufficient investigations implemented before. In the project, we will investigate the detailed Pearl River plume dynamics, and the objectives are listed as follows:
The proposed research will focus on gaining new knowledge on the plume dynamics of the Peal River plume and improve in-situ observation database available to relevant Hong Kong government agencies for related applications. The results of the proposed study will enhance our understanding of impacts of the Pearl River plume on ecosystem of the Hong Kong coastal water, and contribute to regional management efforts.
Using the Peal River plume as an example, the analyses carried out by the project will facilitate understanding of processes of similar river plume systems in other regions.
With so many typhoon passages each year, the Hong Kong coastal area is strongly influenced by extremely strong wind events during the typhoon season. The typhoon related storm surges can induce disastrous inundations in the Hong Kong coastal area, resulting in serious casualty and property loss.? Thus, rapid and precise prediction of the storm surge-induced inundations is of great importance to mitigation of inundation disasters in the coastal area of Hong Kong. Because of the complexity in Hong Kong coastal topography and elevation and the complicated interaction between storm-generated strong ocean currents and the coastal elevation, however, there has been no effective inundation prediction system that could be applied to the Hong Kong coastal area.
This project aims at developing a precise and fine prediction system for storm surge inundation in the Hong Kong coastal area with the satellite remote sensing technology on the platform of open source geographic information system (GIS), incorporating the enhanced Hong Kong coastal digital elevation model (DEM) database to provide an operational inundation forecast system for relevant users. The system will play an importance role in Hong Kong oceanic disaster mitigations.
Scale is a fundamental concept in geography. Although multiscale data, models, etc., are taken into account to study geography, due to scale dependence, the scale mismatching may cause adverse results. Especially, when it comes to the dynamic and interactive geographic process, scale compatibility is becoming much more crucial to decode geographic process.
Serious air quality condition in the GPRD (Great Pearl River Delta) is attracting ubiquitous attentions from both Mainland China and Hong Kong. However, because of the multiscale characteristic of geographic process, air quality process becomes complex and both regional and local effect should be concerned. Numerical air pollution modeling systems have made great contribution to provide a science-based picture, nevertheless scale mismatching considering data, models and visualization may be cause confused results. Thus, multiscale system and scale matching is significant to study and manage air quality problem.
Serious air quality condition in the GPRD (Great Pearl River Delta) is attracting ubiquitous attentions from both Mainland China and Hong Kong. However, because of the multiscale characteristic of geographic process, air quality process becomes complex and both regional and local effect should be concerned. Numerical air pollution modeling systems have made great contribution to provide a science-based picture, nevertheless scale mismatching considering data, models and visualization may be cause confused results. Thus, multiscale system and scale matching is significant to study and manage air quality problem.
Being surrounded by land regions with large population, the South China Sea (SCS) climate variability is closely related to the development and people’s lives in these regions. Being situated between the North Indian Ocean and the western North Pacific, between East Asia and Indonesia-Australia, the SCS climate variability is not only connected to the variability of major monsoons in these regions, but also plays an important role in connecting the variability among these monsoons. The SCS serves as pathway for moisture transport from the North Indian Ocean and the Southern Hemisphere to China. The SCS also serves as a medium linking the remote forcing of El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and tropical Indian Ocean to regional climate in the surrounding regions of dense population. The SCS is also a region of activity of tropical cyclones/typhoons that pose a great threat on coastal southern China, including Hong Kong. There is, however, a lack of systematic study of the SCS climate variability and its remote connections.
The objective of this project is to investigate summertime climate variability in the SCS region and the roles of regional air-sea interactions and remote forcing of the tropical Indian and Pacific Ocean regions. The issues to be addressed include: 1) How the atmosphere and ocean interact in the SCS region and how this changes spatially and seasonally; 2) What are the direct and indirect influences of ENSO on summertime SCS climate and the respective processes; 3) What are the connections of summertime SCS climate with the tropical Indian Ocean climate modes and the respective processes.
The expected outcomes of the research are: 1) The characteristics and processes of air-sea interactions in the SCS region will be unraveled; 2) The roles of regional air-sea interaction and remote forcing in summertime SCS climate variability will be delineated; 3) The processes for different types of ENSO influences on summertime SCS climate will be revealed; 4) The connections between the SCS and tropical Indian Ocean climate anomalies will be identified.
With so many typhoon passages each year, the coastal ocean adjacent to Hong Kong or Hong Kong offshore water (HKOW) is strongly influenced by the extremely strong wind events during the typhoon season. As a strong forcing on the ocean surface, typhoons dramatically alter upper ocean thermal structure, regional circulations, and biophysical properties. In the HKOW, typhoon-induced near-inertial currents are much stronger than tidal currents and can last up to one month after typhoon passage. Furthermore, their strong vertical shear drives vigorous vertical mixing. The response of regional circulation and temperature structure due to typhoons is one of the most important events in the HKOW, and needs more exploration.
The HKOW lacks sufficient investigations, and many basic features of regional circulation and temperature structure remain unclear, especially under the influence of extremely strong winds. The proposed project aims to understand the detailed process of the ocean response to typhoon events that bring gales, heavy downpours, and storm surges to the region, based on frontier ideas and state-of-the-art technologies including field measurements, numerical modeling, and satellite remote sensing. The proposed research will focus on improving the database of in-situ observations in the HKOW, developing a regional ocean model for the HKOW under typhoon conditions with validation by the in-situ observations, and identifying important ocean dynamics affecting response processes. The results of the proposed project will enhance our understanding of dynamical features of the HKOW, and be helpful to developing accurate and validated regional marine environmental prediction systems for utilization under extreme wind conditions.
The project assembles a team of senior oceanographers from local and mainland universities and abroad who have substantial experiences in in-situ observations, numerical modeling and satellite remote sensing studies to ensure the proposed studies achieving a high standing in the international community.
The aim of this research project is to investigate the combined use of optical remote sensing data and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data for the assessment of impervious surfaces (IS) in humid subtropical regions, including seasonal variation, and to evaluate the potential impact of IS on water quality, especially on non-point source water pollution.
With the rapid urbanization of Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta (PRD), the spread of impervious surfaces (IS) has increased dramatically over the last two decades. It has been widely recognized that IS serves as a key environmental indicator since it affects the water cycle, water pollutants and the energy balance and, thus, relates closely to the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. It has also been reported that IS serves an important role in urban socio-economic studies such as detailed population distribution.
Given its importance many methods have been developed to assess impervious surfaces using satellite images, but most of the methods were tested in temperate, continental areas. Few considered the case in humid subtropical areas such as PRD, where there is significant cloud occurrence and different phenology. Due to these differences, difficulties occur when using optical remote-sensing data which is the main data source used in previous studies. Seasonal changes in vegetation, recognized as a key factor in IS estimation, create further challenges. Existing approaches need to be evaluated while additional data sources should be considered in order to establish an advanced assessment of IS in humid areas such as Hong Kong and PRD.
The outcome of this proposed research will provide evidence of the seasonal effects on IS assessment due to phenological change, evaluate the potential of SAR data for improving IS assessment and design a synergistic method to identify IS using optical and SAR images. In addition, the environmental impact of impervious surfaces on water pollution will be assessed. Since the PRD region is highly typical of many fast growing areas, the implementation of this project would serve as a model for other humid subtropical regions of the world.
The South China Sea is a typical monsoon climate region. Every year there are more than ten typhoons or tropical storms affecting the South China Sea including Hong Kong area. Typhoons inject substantial momentum into the upper ocean mixed-layer for a short duration along their passages. Strong typhoon winds generate turbulent entrainment and upwelling that cause subsurface cold water to entrain and uplift into surface layer, resulting in cooling of surface water and deepening of upper mixed-layer. In this study, we propose to use a three-dimensional numerical ocean model, namely Region Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) coupled with an atmospheric model, Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) to simulate the mixed-layer deepening process caused by typhoon in the South China Sea. The objectives of the study are to: 1) investigate the dynamic mechanism of the mixed-layer deepening induced by typhoon through different model schemes, 2) explore the correlation of the mixed-layer deepening with seasonal thermocline depth, and 3) analyze the energy conversion after typhoon passage and the generation mechanism of near-inertial baroclinic waves in the mixed-layer. The results of the proposed study will improve the understanding of the ocean upper layer dynamics under extreme wind condition. This project will be an initiative of a major project for investigating typhoon process.
This project aims to develop a computerized platform for air quality evaluation for Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration and facilitate the knowledge sharing and collaboration in air pollution monitoring and management among cities. The products will contribute to air pollution control and environmental sustainability in the PRD region.
This project will build a collaborative virtual geographic environment (CVGE) platform, establish the list of emission pollutant in this region, achieve an effective integration of multi-source data and models, and design high-performance algorithms for 3D spatial-temporal representation and visualization of air pollutant in urban agglomeration. The integrated system of CVGE with numerical meteorological and air pollution modeling will enable cross-boundary evaluation and high-resolution prediction of air pollution for the PRD region.
Implementation of the project will not only strengthen the collaboration among the governments of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao in air quality monitoring, but also enhance the capability of integrated coping with air pollution with low cost.
To date, it is clear that cooperation among Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao should be strengthened. More research also is essential, specifically regarding the reduction of gross pollution emissions by 8 to 10 percent. In addition, the water environmental protection of PRD has engaged with the Integrative Planning of the Environmental Protection in PRD (2009-2020). This emphasizes strengthening the regional collaborative linkages, constructing an integrative platform of environmental monitoring, and realizing the shared and collaborative management of environmental information among different departments. With this in mind, the study on constructing a unified and synergistic system for water environment analysis in PRD area are proposed as interdisciplinary and comprehensive research using multiple methods and fields. Based on the analysis of the fusion techniques of multisource, multi-date, and isomerous images, a database for integrating remote sensing monitoring data of water quality and quantity, actual measurement data, and relevant basic geographical data (watercourse data, section data, and Digital Elevation Model) will be developed.
Combining the research on general analytical methods and models, the capsulation mechanism of analytical methods and models will be designed. Lastly, using GIS integration techniques, an integrative monitoring demonstrative platform of water quality and quantity will be developed to assist collaborative research and decision making among the functional departments of the three regions. The goal is to promote the sustainable use of the water resources in PRD to achieve sustainable economic development and increase the informatization of the PRD region.
It is of great significance in coastal engineering, marine tourism and sports, marine aquaculture, offshore oil and gas exploitation, marine environmental protection, and coastal disaster prevention to precisely predict coastal ocean dynamic parameters of wave and tidal current. However, there is no effective and practical software system to implement precise forecasts of such marine dynamic parameters for the Hong Kong coastal waters.
The project aims at developing a marine environmental service system based on numerical prediction technology in the nesting domain frame for precise prediction of the coastal dynamic environmental parameters. The objectives of the project are to 1) develop a marine multi-parameter forecasting system under extrema and normal conditions and 2) build an integrated forecasting software under GIS platform.
The sustainable development of industry and economics in the Pearl River Delta region and the rapid growth of population in Hong Kong and South China exert more and more pressure on the environment. One critical environmental issue is air quality, which is directly related to people’s health. Thus, understanding the variability of atmospheric aerosols and the factors and processes contributing to the aerosol variations is of great significance.
As Hong Kong lies on the coast of South China, the air quality in Hong Kong may be related to aerosol variations in South China through the transport of aerosol particles by atmospheric winds. This relation may vary with season following the seasonal change in monsoonal winds. The inter-relationship between air quality changes in Hong Kong and aerosol variations in South China is an issue that will become more and more important due to the increasing connection between Hong Kong and South China’s economic development.
The aerosol-climate connection is complex, including many dynamical, physical, and chemical processes. Aerosol can lead to changes in atmospheric dynamics and thermodynamics by modulating the transfer of solar radiation in the atmosphere. Precipitation can flush out aerosols and atmospheric circulation can lead to transport and accumulation of aerosols. There could be different types of relationships between aerosol and cloud/precipitation variations. Delineating the inter-relationships between aerosol and regional climate change is of great interest to both climate scientists and the public.
The objective of this project is to investigate the inter-linked variations of air quality and aerosol in Hong Kong and South China and its relationship to climate change in the Pearl River Delta region. The key issues to be addressed include: 1) The variability of atmospheric aerosols in South China; 2) Relationship between Hong Kong air quality and South China aerosol variations; 3) Relationship between aerosol and regional climate change in the Pearl River Delta region.
The proposed research is expected to have the following outcomes:
1) Illustrate the spatial-temporal characteristics of interannual variations of aerosols around South China; 2) Reveal specific atmospheric states leading to inter-related air quality and aerosol variations between Hong Kong and South China; 3) Delineate different types of aerosol-cloud-precipitation relationship in the Pearl River Delta region.
Previous studies testing the association between the built environment and walking behavior have been largely cross-sectional and have yielded mixed results. This study reports on a natural experiment in which changes to the built environment were implemented at a university campus in Hong Kong. Longitudinal data on walking behaviors were collected using surveys, one before and one after changes to the built environment, to test the influence of changes in the built environment on walking behavior.
Built environment data is from a university campus in Hong Kong, and includes land use, campus bus services, pedestrian network, and population density data collected from campus maps, the university developmental office, and field surveys. Walking behavior data were collected at baseline in March 2012 (n=198) and after changes to the built environment from the same cohort of subjects in December 2012 (n=169) using a walking diary. Geographic information systems (GIS) was used to map walking routes and built environment variables, and compare each subject’s walking behaviors and built environment exposure before and after the changes to the built environment. Walking behavior outcomes were changes in: i) walking distance, ii) destination-oriented walking, and iii) walked altitude range. Multivariate linear regression models were used to test for associations between changes to the built environment and changes in walking behaviors.
Greater pedestrian network connectivity predicted longer walking distances and an increased likelihood of walking as a means of transportation. The increased use of recreational (vs. work) buildings, largely located at mid-range altitudes, as well as increased population density predicted greater walking distances. Having a greater density of work buildings at lower altitudes deceased subjects’ walked altitude range, while having more bus services and a greater population density encouraged people to increase their walked altitude range.
In this longitudinal study, changes to the built environment resulted in changes in walking behaviors. Use of GIS combined with walking diaries presents a practical method for mapping and measuring changes in the built environment and walking behaviors, respectively. Additional longitudinal studies can help clarify the causal relationships between the built environment and walking behaviors identified in this natural experiment.
The objective of this project is to provide early-waring service before geo-hazards occurrence based on high accurate, large-scale land subsidence derived by PS-InSAR technologies. We plan to develop an efficient PS-InSAR (Persistent Scatterers SAR Interferometry) processing platform and early-warning system. With the aid of deformation models development and integration, the platform is capable of providing deformation and early-warning information for city groups, high-speed transportation lines as well as instable slopes which cannot be found in any of the software tools in the market.
Based on the already developed technologies, the integrated PS-InSAR platform developed in the university will overcome the A-PSI limitations (e.g. sparse and low quality PS candidates in sparse vegetation slopes, weak monitoring capability for large-scale linear features and city groups) through model modification and optimization. We plan to introduce parallel computation technologies, conquer the key technologies including multi-source SAR data cross fusion, new-style PS model development, GIS-based simulation and intelligent decision, to serve large-scale geo-hazards investigation as well as linear structures deformation monitoring.
The developed platform will offer ground subsidece surveillance of Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta (PRD), which is significant for geo-hazards early-warning & intelligent decision, providing technical solutions for satellite earth observation, software development and add-valued product dissemination in Hong Kong.
As part of the large warm pool extending from the eastern Indian Ocean to the western Pacific, the South China Sea (SCS) displays prominent atmosphere-ocean interaction as that in the western North Pacific and tropical Indian Ocean. This interaction may play an important role in the regional climate variability. Climate model is an important tool for understanding the climate variability and predictability as well as the climate change. The applicability of this tool depends on the performance of the model in various aspects, including the atmosphere-ocean relationship in different regions. It is important to evaluate how the climate models perform in the SCS region, which will give important guidance for limitations and uncertainties that need to be considered when using climate model to monitor and project climate in the surrounding regions. The SCS climate variability is likely linked to that in the densely populated neighboring regions and to the East Asian winter (EAWM) and summer monsoon (EASM) variability. Anomalous EAWM can induce SST cooling in the SCS. As the SCS SST is modified, it may induce anomalous heating and change the thermal contrast with the land region, which may contribute to climate variability in a large region.
The objective of this study is to enhance the understanding of the atmosphere-ocean interactions in the South China Sea region and the connection of South China Sea climate with the East Asian monsoon variability. Key issues being addressed are: 1) How do the atmosphere and ocean interact in the SCS region? 2) How is the performance of climate models in simulating the atmosphere-ocean relationship in the SCS region? 3) What is the relationship of the SCS climate variability with the EAWM and EASM variability?
Possible outcomes of this research are: 1) The regionality and seasonality of nature of air-sea interaction in the South China Sea region will be revealed; 2) The strength and weakness of climate models in simulating the air-sea relationship in the South China Sea region will be identified; 3) The connection of the South China Sea climate to the East Asian monsoon will be revealed.
With the initial success of the Satellite Remote Sensing Ground Receiving Station of CUHK, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) has authorized the CUHK Station to receive the latest China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS-02B) data.
The CBERS-02B Satellite was launched on 19 September 2007. It equips with 20m multi-spectra cameras and a brand new 2.7m optical high resolution panchromatic camera.
With the new CBERS-02B acquisition capability, the CUHK Station can monitor the environment of Southern China as well as Southeast Asia with multiple satellite, multiple spectral bands and in all-weather conditions.
With CNSA’s supports, this proposed project aims:
The project will develop massive, timely high resolution satellite data products to support environmental monitoring applications in the region. The data products will also bring new business opportunities for the local industries to provide professional services to the prospective clients in China as well as Southeast Asia.
The purpose of this proposal is to investigate the relationship between remotely sensed surface latent heat flux and coastal earthquakes and typhoon intensification.
Amongst natural hazards, earthquakes and typhoons are the deadliest and most damaging. Earthquake occurrence is also by far least predictable. The prediction of Typhoon tracks using numerical weather prediction models has reasonable success. The intensity forecast remains a formidable challenge. This project can contribute to understanding the use of SLHF in coastal earthquake prediction and typhoon intensification.
Urban ground deformation (e.g. subsidence or landslide) is a serious environmental hazard associated with rapid urbanization in many parts of the world and more than 70 cities in China are undergoing natural or human-induced land surface subsidence.
Compared with traditional ground-based surveys (e.g. GPS and spirit leveling), satellite Persistent Scatterers Interferometry (PSI) is a very promising remote sensing technology that offers low cost, large-coverage deformation monitoring and up to millimeter accuracy by exploiting long series of SAR data acquired over the same monitoring area. Due to the outstanding availability of data more than 12 years, PSI has been mostly and successfully applied to a time series of SAR data acquired by compatible radar sensors of the European Remote Sensing Missions ERS-1 and ERS-2. But the ERS-1 mission ended in year 2000 and unfortunately, recent ERS-2 SAR acquired images are no longer suitable for interferometric applications due to the failures of gyros since later 2001. With the launch in 2002 of ERS-2 successor, ENVISAT satellite, therefore updating ERS-based PSI measurements by means of the Advanced SAR (ASAR) data of ENVISAT mission became a major issue. Moreover, in many cases the current time PSI monitoring is in the center of the interest, but the existence of the ERS archive is relevant as a record of the deformation history. Another important factor is that the reliability and accuracy of current time monitoring with ASAR is improved by the availability of the historic ERS observations, this particularly in cases where only few ASAR images were acquired. For these reasons, it is extremely important to study ERS-ENVISAT coherent integration in PSI analysis for the continuity of ERS-based deformation measurement and the improvement of ASAR-based monitoring accuracy.
In last thirty years, land subsidence has become one of the major geological disasters in urban areas in China. It is said land subsidence occurs in more than 90 cities in China. In Hong Kong, land subsidence has also been a problem mostly concerned in the reclaimed land from sea. Monitoring the land subsidence efficiently will not only help people identify the spatial and temporal pattern of this kind of disaster, but also guide people minimize the hazard ahead. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) has been recognized as the most powerful tool to monitor the land subsidence in long time series and in large scale. However, it also has shortcomings. The PS is very hard to be detected in vegetable area. In PSI approaches, PS selection is the most difficult but important stage, the number and quality of PS directly affect the computed deformation result. All of the PSI approaches do not use the polarimetric information to select PS. In this project, a new PS selecting algorithm for monitoring the land subsidence by means of PSI associating with Polarimetry. The new algorithm is developed using not only the amplitude dispersion, spectral phase diversity, temporal and spatial coherent value but also polarimetric information. The physical characteristic of selected PS in urban area will be studied at the same time. And we will use the PS to be selected by the developed algorithm to estimate the deformation in urban area. Finally the field research will be executed to validate the results.
In the foreseeable future transgenic rice will be ready for commercialization, including varieties with higher yields, greater tolerance of biotic and abiotic stresses, resistance to herbicides, improved nutritional quality, and novel pharmaceutical proteins. But GM rice has generated great concerns about transgene movement to landraces and wild relatives in centers of origin or diversity, and its genetic, ecological, and social consequences.
We propose to develop a new approach to monitor the growth and gene flow of genetically modified (GM) rice. The primary objectives of the proposed research are to: 1) measure the hyperspectral reflectance of GM rice plants and analyze its spectral properties; 2) evaluate the ability of hyperspectral data to discriminate between GM rice and non GM rice; and 3) monitor gene flow from GM rice with Green fluorescent protein as a marker through analysis of hyperspectral properties of fluorescent protein.
The deliverables from the project should greatly contribute to establishment of a time and cost effective system for monitoring the growth and possible gene flow of GM rice, and can promote the development of remote sensing and gene biology technology in monitoring genetically engineered crops in the environment.
The objectives of this proposal are:
To investigate optical properties in the coastal region of Hong Kong and Taihu Lake of Mainland. Based on the monthly measurement of the optical properties in the coastal waters and Taihu Lake, the variation of seasonal cycles of water quality variables will be understood. As a result, the changes in water quality information can be assessed and updated using MODIS data. Furthermore, to compensate for the effects of different temporal/spatial resolutions, other satellite optical data, such as Landsat-TM, SPOT, AVHRR, SeaWiFS, and MERIS data will be evaluated as a complement in this proposed project.
To monitor physical properties in the coastal region of Hong Kong and Taihu Lake. Cloud cover and rainy conditions seriously limit the usefulness of optical satellite data for the monitoring of coastal waters and inland lakes. To overcome the limitation of cloudy and rainy conditions, ASAR data will be applied in all-weather conditions to retrieve and monitor the wind field and waves in the study areas. ASAR data will also be used to detect oil slicks and algal blooms in the coastal region of Hong Kong, and cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake of Mainland.
Recent intensified severe air pollution problem in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region, caused by the fast increasing industrial development, has become the top environmental issue for cities in the region including Hong Kong. Air pollution control is critical for the sustainable development. It is possible to tackle the problem by cooperative measures taken by all stakeholders in the region. As a step forward to help alleviating this problem, we have proposed to develop a computerized platform to support the collaboration among cities in the PRD region for air pollution monitoring and management.
The aim is to develop a collaborative virtual geographic environment (CVGE) platform to study the environmental issue from a geographic viewpoint based on a successful VGE developed from a previous funded project by the research team. Instead of using a database oriented geographic information systems (GIS), the present approach is an integrated internet-based model management platform with geo-database support. This platform provides a geo-collaborative working environment in which dynamic processes such as pollutant dispersion are presented for various research partners to study improving methods. Simulation studies using the CVGE and data from the region will help identifying causes of severe pollution episodes leading to feasible corrective measures.
Urban ground deformation is serious environmental hazard in Hong Kong and the Mainland China. More than 70 cities in China are undergoing natural or human-induced subsidence. The disaster can led to significant damage and, driven by safety and legal liability, construction and civil engineering industries have great demands on land surface movement monitoring, especially in major cities of China.
Satellite Permanent Scatterers Interferometry, (PSI) is a promising technology that offers low cost, large-coverage deformation monitoring and up to sub-millimeter accuracy. However, due to insufficient archive images available to many China and Asian cities, PSI can hardly be widely applied in the region. This proposed project aims to develop the Advanced PSI (A-PSI) to overcome PSI’s limitations in the region. A-PSI relaxes the PSI’s constraints and can be applied in linear or non-linear deformation (e.g. landslide) scenarios. Moreover, A-PSI can also be applied to areas of interests even with a limited SAR archive images (e.g. China and other countries in Asian). The developed technologies and services can be adopted by the various players in the local construction industry including public and private organizations and will bring new business opportunities to the local industry to engage the engineering consultancy business in China.
This dataset is a database outcome of the Research Project entitled "Beijing in Transition: A Historical GIS Study of Urban Cultures, 1912-1937." Supported by the Research Gant Council of the Hong Kong SAR Government with the project code number #450407, the research project aims at examining the spatial patterns of modern urban cultural change in China. The object of observation is set in this project at the Beijing city from the advent of the Republican era in 1912 to the outbreak of the Sino-Japanese War in 1937. Beijing city represents a good case where traditional and Western cultures encountered and intermingled with extraordinary intensity under the political cultural vacuum of either a weak central government or as a provincial city during the Nanjing regime.
The project has three objectives:
The six cultural spheres are as below:
Information collected in this dataset is from the public domain, either online or by request on site. Those from the Beijing Municipal Archive constituted the main body of the dataset but there were also data from other libraries, archives and museums. The sources of the data were also noted in the attribute tables and other materials presented in the Online Resources in the Homepage.
This dataset may support research in various disciplines, including history, urban study, historical geography, historical GIS study, archival study, economics, law and legal history, religious study, education history, public health and new cultural history, and so on. It promotes interdisciplinary inquiries.
Project investigators would like to thank Beijing Municipal Archive for its very professional staff’s considerate assistance during the entire process of our data collection; and to Rockefeller Archival Center for their support in our research regarding Peking Union Medical College. In particular we would thank them for their kind permissions to let us and our users use their information, including the rare old Beijing maps in their possession.
Wetlands play an important role in bio-geochemical cycling, flood control and recharging of aquifers. The wetlands of Pearl Delta Region (PDR) and its adjoining areas support a variety of crops, for example, sugarcane, banana, lotus, and so on, which are important economic crops in pearl delta region. Precise information of their nature, extent and spatial distribution is important for monitoring the biological condition of costal wetlands. Synthetic aperture radar, which has the ability to penetrate cloud, permits regular and repetitive observation of the wetlands.
We propose to develop a new approach to carry out the wetlands mapping using multi-temporal microwave remotely sensed data. The primary objectives of the proposed research are to: 1) Improve coastal wetland characterization (cover type and fraction of vegetation, soil and water estimate) using field data and optical and radar remote sensing data; 2) Investigate radar backscattering process associated with each types of the coastal wetlands; 3) Identify optimal combination of radar data (with different polarization and incidence angle) for coastal wetlands classification; 4) Develop a new classification method for wetland mapping; 5) Evaluate the quality and reliability of all products developed from this project using field data, optical data, and other independent reference data.
Deliverables from the project should greatly contribute to a better understanding of coastal wetlands ecosystems and towards establishment of a long-term monitoring capability in the South China-Sea. Because the wetlands of South China-Hong Kong region is typical of many wetland ecosystems in the world tropical and subtropical regions, especially areas under consistent clouds and rain, implementation of this project can serve as a template for many regions of the world.
Urban ground deformation is serious environmental hazard with rapid urbanization in Hong Kong and the Mainland China. More than 70 cities in China are undergoing natural or human-induced subsidence. The ground deformation hazards threaten human activities and cultural heritage, thus influencing the socio-economic conditions of a city. Driven by safety requirement and legal liability, local/regional government and civil engineering industry have great demands on ground displacement monitoring, especially in major cities of China.
Satellite Permanent Scatterers Interferometry (PSI) is a promising radar remote sensing technology that offers low cost, large-coverage deformation monitoring and up to sub-millimeter accuracy. However, due to insufficient archive images available to many China and Asian cities, PSI can hardly be widely applied in the region. Moreover, the constant-velocity deformation model also limits PSI to identify non-linear deformation behaviour, for example, for the landslide monitoring. This proposed project aims to develop the Advanced PSI (A-PSI) to overcome PSI’s limitations in the region. A-PSI relaxes the PSI’s constraints of availability of SAR data and can be applied in linear or non-linear deformation (e.g. landslide) scenarios. The developed technology can be applied to areas of interests even with a limited SAR archive images (e.g. China and other countries in Asian) and can improve precision and reliability of the estimation of deformation parameters.
Hong Kong is surrounded by potential oil pollution sources: harbors, ports, and navigation water ways with ten thousands of ship’s come-and-go every year, offshore fishery grounds, and offshore oil and gas drilling and exploration around Hong Kong in South China Sea (SCS). Recently, large areas of oil films have frequently appeared around Hong Kong waters, and formed a severe threat to the marine environment. Previous studies have showed that SAR imaging is an effective approach for monitoring of oil slicks on the coastal water and ocean surface.
Red tide may cause a destroyed disaster to marine aqua-culture and may severely destroy marine environment. The coastal waters along South China Sea including Hong Kong waters are the ocean areas favorable for red tide (or algal blooms) because of warm weather and eutrophication. Previous studies have demonstrated that optical imageries are effective for monitoring of red tide in the marine environment. But SAR data should be useful for monitoring red tide in the case when optical images are limited in the cloudy and rainy situation. Therefore, oil spill detection and red tide monitoring using ASAR and optical data are critical research topics in the coastal region around Hong Kong and its vicinity.
This proposal addresses the impact of aerosol on precipitation on the Pearl River Delta regions from a remote sensing perspective. Remotely sensed information, when carefully calibrated, can provide large area coverage and timely information at reduced cost. The suitability of remote sensing data for monitoring the aerosol and precipitation in the region is investigated. The presence of aerosol reduces the reflected radiation, but may heat the absorbing layer, hence stabilizing the region and thus reduce rainfall. Another mechanism is the so call “Elevated Heat Pump” effect that the heating due to aerosols heat the layer and acts to induce convergence at the surface. This large scale convergence mechanism has been shown to induce early on-set of the monsoon in the Indian subcontinent. This project will first establish the regional climatology of aerosol, precipitation, and other cloud parameters and related to in situ observations. Trends will be detected using the Empirical Mode Decomposition technique that can delineate other climate signals. Seasonal, non-seasonal changes and long-term trends will be investigated and factors contributing to these variations will be discussed.
Fishery accounts for 23% of agricultural production in PRD. However, with the increasing environmental crises in Southern China, ocean disasters such as red tide, oil spill and other ocean pollution problems become serious threats to the fishery.
This project is a co-operation between the Chinese University of Hong Kong and the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology (SCSIO) of Chinese Academy of Sciences. It aims to develop innovative technologies for near real time monitoring and warning of ocean disasters.
With the CUHK’s Satellite Remote Sensing Receiving Station and SCSIO’s disaster warming models as the foundations, the Project Team will develop new multi-dimensional dynamic monitoring methods, scientific workflow management and intelligent information extraction techniques. We will also integrate the technologies and develop ASP services for near real time ocean disasters analysis and warning. The GuangDong Provincial Oceanic and Fishery Administration has agreed to use the ASP services and will provide us the evaluations.
This project not only develop innovative technologies for the fishery in PRD, as the Remote Sensing Data are captured and distributed in CUHK, the project will also help the Hong Kong Information Technology Service Providers to open the new market of fishery / ocean information services.
In the foreseeable future genetically modified (GM) rice will be ready for commercialization, including varieties with higher yields, greater tolerance of biotic and abiotic stresses, resistance to herbicides, improved nutritional quality, and novel pharmaceutical proteins. But GM rice has generated concerns about transgene movement to landraces and wild relatives in centers of origin or diversity, and its genetic, ecological, and social consequences.
We propose to develop a new approach to monitor the growth and gene flow of GM rice. The primary objectives of the proposed research are to measure the hyperspectral reflectance of GM rice plants and analyze its spectral properties, evaluate the ability of hyperspectral data to discriminate between GM rice and non GM rice and monitor gene flow from GM rice.
The deliverables from the project should greatly contribute to establishment of a time and cost effective system for monitoring the growth and possible gene flow of GM rice, and can promote the development of remote sensing and biology gene technology.
Asthma is important global health problems. Some 300 million people are living with asthma. It is an allergic condition characterized by an exaggerated response of the body’s immune system. Although there are genetic factors which predispose to the development of asthma, exposure to certain environmental factors may contribute significantly to the risk of developing the disease. Allergic individuals develop asthma attacks when there is a trigger, which can be an allergen or an irritant. The following will give some detailed information on current research on asthma from the aspects of environmental factors. The environmental risk factors for asthma originate from the hygiene hypothesis which was put forward in 1989. Early life environments, indoor air pollution and outdoor air pollution are the three main aspects discussed.
Impervious surface has been recently recognized as an important environmental indicator that characterizes the development of urban and suburban environments. The objective of this project is to develop a new approach for impervious surface percent (ISP) mapping and investigate its application in urban studies. The overall research plan includes: (1) develop a new method for ISP mapping using both optical and InSAR data; (2) investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of urban change detection using ISP mapping; (3) explore the forming mechanism of UHI by quantitatively investigating the relationship between UHI and urban landscape features including impervious surfaces, topographic relief, vegetation and water coverage, etc.
Ocean is not only mankind's living space and treasure trove of resources, but the national defense outpost of many coastal countries as well and virtually plays the most significant role in economic, political and military development. The measurement and analysis of the marine environment is fundamental to the management, research and development of ocean. The amount of ocean environment data collected has seen a rapid increasing with development of data collecting technology, which especially includes the advent of satellite remote sensing. GIS acts as tools to gather, manage, analysis and visualize these data, and are now growingly applied to the marine field. However, the traditional commercial GIS may have problems and remain in its contributions. These problems are mainly rooted in the unsuitability between the data model of traditional GIS with multi-dimensionality dynamic nature of ocean environment. Therefore, a spatial-temporal data model which can model the multi-dimensional dynamic data of ocean environment and support analysis and visualization function of these data becomes a necessity for the development of an effectively marine GIS system. This research is aimed at developing a Marine Spatio-Temporal Data Model (MSTDM) based on generalization of the spatio-temporal distribute pattern of ocean environment data, include in situ data and satellite remote sensing data. The model is expected not only to be used to describe the multi-dimensional dynamic ocean environment, but also to support particular analysis and visualization functions used in the oceanography community.
Hong Kong has a long history of landslide disasters. From the Government’s records, there are 57,000 register slopes and 39,000 of those were constructed before 1977 which the safely standards are considered to be insufficient nowadays. The Government had put considerable efforts and resources to improve the slope safety. However, the progress of slope improvement works is still slow and only 3,500 high priority pre-1977 slopes can be improved by 2010.
Remote Sensing Satellite and the Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) are the promising technologies to monitor small land surface movement over extensive areas and with extremely high temporal resolution. However, current technologies are considered as “post-event” analysis which the results can be obtained after days or weeks of computation. This proposed research aims to improve the computation methods such that the InSAR analysis results can be produced in near real time domain (i.e. within 12 hours of computation).
The project team proposes to address the challenging issues through studies the bottlenecks of the current computation methods and the optimal use of the radar data received by the CUHK Satellite Remote Sensing Receiving Station. Two or more radar images acquired over the same slope will be analyzed using a specific InSAR approach in order to reveal subtle movement on the ground surface. The InSAR results will be further analyzed using the Geographic Information System (GIS), with its database consisting of DEM, aerial photographs ,and other geological information, to generate a wide range of value-added products such as geological profiles, contour map, animation, three dimensional view, and flythrough of the study area.
Outcomes of the proposed research include operational procedures for near real-time operation of radar InSAR based on previous works done by PI and Co-Is. These outcomes will be easily applied in slope monitoring and ground deformation in Hong Kong and neighboring areas.
China’s poor record of underground mine safety has been challenging the tolerance of the society. New methods are needed to monitor those risky mining areas in addition to the improvement of the administrative system. The CUHK’s newly constructed high performance satellite data ground receiving station which will become operational at the end of 2005 can be effectively used to assist mine management. We propose to address the critical safety issues through near-real time monitoring of ground surface subsidence due to underground mining by an optimal use of the radar data received by this station. Two or more radar images acquired over the same mine site will be analyzed using an Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar processing system (InSAR) in order to reveal subtle changes on the surface of ground in the affected area, which would otherwise be impossible to obtain using optical satellite data due to presence of cloud and/or vegetation cover.
The results form the InSAR data processing will be further analyzed using the Geographic Information System (GIS), with its database consisting of DEM, lithological characters, and other geo and mineral information, to generate a wide range of value-added products such as geological profiles, contour map, animation, three dimensional view, and flythrough of mine subsidence. The purpose to develop such GIS-based InSAR system is to monitor illegal mining activities (such as illegal underground demolitions) and to prevent mine disasters in additional to subsidence monitoring in China. A range of data compression methods and high speed data processing algorithms will be developed and implemented in software tools in order to deliver the above products in near real-time.
Outcomes of the proposed research include operational procedures as well as relevant software tools for near real-time operation of radar interferometry based on previous works done by PI and Co-Is. These outcomes will easily find other applications such as monitoring flood, storm surge, landslide, oil spill, and ground deformation in Hong Kong and neighboring areas.
The coastal wetland bordering the South-China Sea is one of the most important ecosystems in the world with diverse species of plants and vertebrate, and bears social and economic significance to the large population living in this region. Unfortunately, the total area of the wetlands in this region was significantly reduced and the quality deteriorated over the last several decades, due to fast population and economic growth and excessively conversion of wetlands into other land use.
We propose to develop a new approach to quantification of coastal wetland biophysical conditions in the Pearl River Delta region through an integration of optical and microwave remote sensing, modeling and in-situ measurements. The primary objectives of the proposed research are to: 1) improve coastal wetland biological condition characterization using field data and optical and radar remote sensing data, 2) investigate optical spectral reflectance and radar backscattering process through modeling technique for each component of the coastal wetlands, 3) develop a new inversion method for costal wetland biophysical parameter retrieval , and 4) evaluate the method and data products using field and other independent reference data.
The deliverables from the project should greatly contribute to a better understanding of coastal wetlands ecosystem and towards establishment of a long-term monitoring capability in the Pearl River Delta region. The research will also contribute to bridging the relations between the remote sensing technique and the wetland ecology.
Provide trainings, supports, teaching materials (including Remote Sensing Data and Software) and free Internet-based Remote Sensing Resources for geography teachers to incorporate satellite remote sensing technology in the Geography teaching.
Geography and students of secondary school
Expected Number of beneficiaries: Up to 10 partnered secondary schools in the first stage of the project and 30 secondary schools in the second stage. And 370,000 student and teachers in long-term.
Duration: 20 months
Collaboration with other parties / partners:
Computer-assisted learning material using Satellite Remote Sensing Images and Software coving the subject e.g. water quality monitoring; global climate change; rain forest, urban study, land use of Hong Kong; Land cover changes.
As a collaboration between the Institute of Space and Earth Information Science, CUHK and Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute (長江水利委員會長江科學院), this project aim to maintain an ASAR Remote Sensing Data Centre for flood control and monitoring for the Changjiang Area and to conduct the related researches and technological developments. Specific tasks of the centre include: develop data products and services market; joint project application; research and academic exchanges; prompt the uses of ASAR data in environment monitoring; ecological protection and disaster prevention etc.
During the initial establishment of the centre, three researches projects had been commenced:
Land use and land cover (LULC) change is recognized as one of the largest and most convincing mechanisms of the global change and plats critical roles in a wide range of earth system processes. It has been hypothesized that LULC change could play equally important role in affecting global climate as does the increased CO2. At present, however, such impacts are poorly understood at regional to global scales, primarily because accurate and effective methods for large-area LULC change detection have yet to be developed.
We propose to conduct an integrated assessment of LULC change and its impacts on climate in the Greater Pearl River Delta (G-PRD) region of southern China. The overarching goals of the project are:
This research not only possesses great scientific merits, but also provides vital information for formulating strategies for a sustainable development of the G-PRD region. Because this region is typical of many fast growing coastal areas, particularly in developing countries, implementation of this project can serve as a template for studies of other regions around the world.



Paddy rice accounts for about 42% of the Mainland China’s total agricultural production. An effective management of paddy rice production is the key to address China's as well as global food security issue. Besides, with China's entry to WTO, a scientific methodology to paddy rice yield estimation is essential to the nation's agricultural planning and policy making.
Paddy rice is indigenous to warm and humid environment and it is impractical to use optical remote sensing satellite in those cloud-prone and rainy regions. "All-weather" Radar Remote Sensing becomes the only possible satellite data source. This project, collaborating with the Ministry of Agriculture of PRC, targets to build a comprehensive methodology for paddy rice classification, growing parameters retrieval algorithm and yield estimation.
The developed methodology can be adopted readily in rice growth monitoring and yield estimation for most paddy rice fields interested by local governments and private agricultural companies. Besides, the products also provide a valuable reference to the investors of global rice futures market. This proposed project will open new business opportunities to the local Hong Kong companies.
Most paddy rice in southern China grows in warm, humid and rainy areas where it is hard to acquire optical remote sensing data. The proposed research plans to take rice growing area in Zhu Jiang river delta as test site. Temporal ASAR data Backscatter behavior of Rice are researched to find better combination of ASAR data of different imaging parameters to map the acreage of rice growth. The ground measurements are also collected at the same time during the acquisition of ASAR data, including bio-physical parameters of rice. And then a semi-empirical backscattering model is designed to calculate leaf area index (LAI) of rice in the area using ASAR data so that the model can be used indirectly to estimate rice yield. The research outcome will provide a systemic method to estimate rice growth acreage and yield using ENVISAT ASAR data in cloudy and rainy area. Because rice is also the staple grain in southeastern Asia, the research result could be used in this area.
The overall objective of the project is to develop a suite of new methods to address several key problems in land use land cover change detection using remotely sensed image data. These methods include: (1) a new radiometric data normalization algorithm that is robust to outliers; (2) a novel image segmentation method for changed area extraction from difference image; (3) an improved image classification scheme combining SVM and MRF for change type identification; (4) a new strategy for change detection using SAR images by synthetic analysis of multiple image features. These methods can form a complete work flow for remote sensing change detection, and will be applied to detect and quantify LULC changes in the Great Pearl River Delta region over the past decades.

In October 2004, The Sustainable Development Unit (SDU) of the Administration Wing of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government (HKSARG) commissioned a study to update the Terrestrial Habitat Mapping and Ranking for Hong Kong based on conservation value using the latest remote sensing and geospatial data and data collected from field survey.
The Joint Laboratory for GeoInformation Science (JLGIS), The Chinese University of Hong Kong, in association with Scott Wilson Ltd, submitted a proposal and was later chosen by the SDU among several organizations to carry out this study.

After a four- month dedication to the project by a team consisting of professors, technicians, field surveyors, and graduate and undergraduate students from the CUHK and partners, all tasks were successfully completed by the end of March 2005. The project major deliverables include:


This Study provides the most up-to-date information with regard to habitat types and conservation values for Hong Kong. The habitat map, as one of the key deliverables of the project, allows for quantification and assessment of existing natural habitats and study of its status and trends when compared with the habitat maps developed in the previous studies. The conservation ranking map for each habitat portrays in detail areas with various levels of conservation status, and provides useful information for sustainability assessment.

The field database not only includes information on habitat type and status, but also detailed information on plant species and communities and the importance regarding conservation of different habitat types. The 360-degree panoramic photos along with GPS location provide a first-hand dataset for each site surveyed.


Hyperspectral remote sensing takes advantage of new detector technology to permit the extension of ground-based spectrometers into the air on moving platforms. Thus, the distinct value of obtaining continuous spectral plots that measure reflectance from the ground, water, or the atmosphere has opened up the possibility of acquiring detailed data on the materials and classes present on the Earth's surfaces, so that rigorous analysis of their compositions over large areas is now feasible.
With rapid urban development in Hong Kong area, its subtropical environment is increasingly vulnerable to human impact. Therefore, it is necessary to establish reliable and effective mechanisms for monitoring of environment in Hong Kong area since the preservation of environment resources is very important for sustainable development of Hong Kong.
Hyperspectral remote sensing has the potential to offer a timely and cost effective method for deriving information of environment resources in vast areas, its applications will provide us with a powerful tool for monitoring of environment resources in Hong Kong area.

Geological disaster study has great significance in the world nowadays, especially in developed area, such as in Hong Kong. Hong Kong is a hilly region, and has a typical characteristics of structure controlled topography. Earthquake and landslide are the most important study projects. When land surface, which composed of the rock body or the soft sediments, loosed balance, landslides will happen in the area.
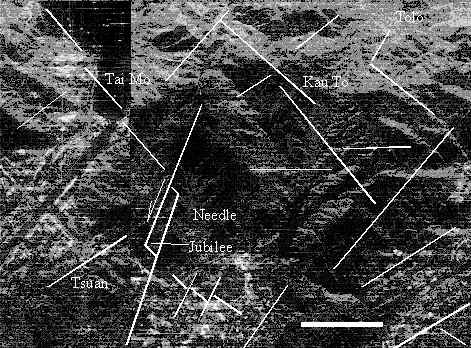
The control factors of landslide are the Neotectonic activity, the physical condition of basement rock , the underground water action and the micro-topography. In order to understand the mechanism of landslide, radar-geology study will get information both from radar image processing nd field investigation. By computer processing, we can get second and third order structure lamella from image as well as their relationship. By field investigation, we can get macro-structures, Neotectonic acting faults, such as open crack and extension faults as well as the physical condition of the rocks, and the information of the underground water action by further study.
Put all these data together, and supported by GIS, we can make the radar-geology model of the landslides. The model can be used in precaution and forecasting landslides, and reporting the possible position of landslides. The model can also be prepared for seismic risk, land use and city construction.
The main purpose of a marine chart is to give a schematic representation of a submarine relief according to the scale of the chart and its purpose. Therefore, the goal of chart generalisation is to produce charts which are as close as possible to reality while ensuring the legibility of the chart and mostly the safety of the user. In our work, we focus on the generalisation of isobathymetric lines (contour lines) for maritime charts (figure 1). Currently, this operation is mostly performed manually however, with the arrival of new sounding techniques and the increasing amount of data, new techniques must be developed as manual processing is no longer conceivable.
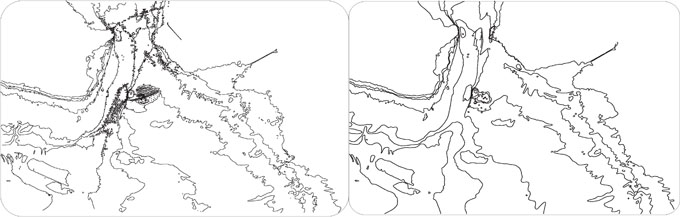
The main constraints that have to be respected during the process are the legibility constraint (a minimal distance must be observed between the lines so that information can be properly read) and the safety constraint. That means that on a chart, the indicated depth must never be deeper than the real depth so that the sailor will not try his way in a too shallow area (Figure 2). As a consequence, an isobath can only be deformed or displaced towards greater depth and an isobath characterising a peak must be maintained.

The objective of the project is to define a set of algorithms and to combine them in order to perform the different generalisation operations. The research work is conducted in three different parts: (1) definition of a smoothing operator; (2) definition and combination of different generalisation operators; (3) definition and validation of a generalisation strategy.
The smoothing operator is based on a snake model. The principle is to reduce the overall curvature of the isobath in order to remove oscillations and sharp angles. Two points are taken into account. The safety constraint imposes that deformation are performed towards greater depths so that the resulting curve is entirely located on the side of greater depth. Visibility conflicts such as cusps or curve segments which are too close must be corrected by removing some segments in order to ensure the legibility of the result (Figure 3).
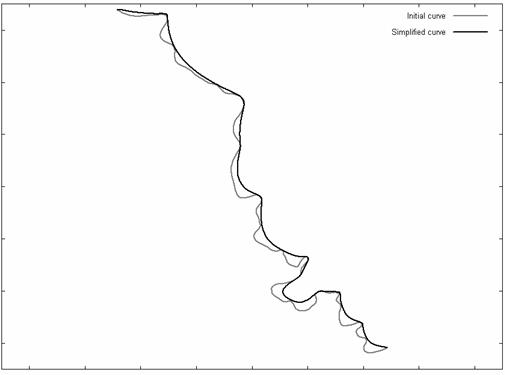
Based on this operator, an aggregation and a displacement operators have been defined. Combined with an enlargement and a deletion operators, they provide a set of operations for cartographic generalisation (Figure 4). The last stage is to define a strategy, i.e. a set of rules to decide which operator to apply. For that purpose, spatial relationships between the isobaths and some quality estimators must be defined. The quality estimator is used both to choose the operators and to validate the process by estimating the deformations done to the surface defined by the isobaths.

Please contact Dr. Eric GUILBERT for further information.
Please click here to download the project details.
Please click here to download the project details.
Please click here to download the project details.
This system is designed for Environment Protection Department to monitor the location of Red tides. The main function of this system is to visualize the location of red tides in form of map. So, user can be easier to find out the effect of the red tides towards certain area.
By the Querying function, users can enter in certain parameter to find the desired cases on the map. Moreover, the further limit function can give user to scan out the unnecessary information in order to increase the efficiency. It is a user-friendly system since it does not required any specific skill in GIS or to use the software.
Basically, the querying system is in form of form filling. On the other hand, the user without any technique in map drawing or database management can update this system. User can simply click certain button to update the map by its own. After that, the database of the new item can be inserted through form filling.
Spatial objects that are represented in a conventional GIS are generally considered to be crisp and represented by determinate boundaries. When objects change gradually and continuously over space, there are no crisp boundaries to differentiate them. They are called fuzzy objects, which have indeterminate spatial extent and boundaries. The concepts of fuzzy spatial objects have been proposed and applied in a coastal geomorphological ase of the Netherlands (Cheng, 1999). How to apply these concepts in other application domain (social & economical phenomena) needs further investigation although the concept doesn't exclude other application fields.

Therefore, the objectives of this study are further application (in terms of cases) and development of the fuzzy object concepts (in terms of different data sources). The key issue is to define the objects of interests in the application domains and build the procedure to extract the object from testing data sources.
The following figures present the case study of extracting land cover types of Hong Kong from TM images. We apply the SMA (spectral mixture analysis) method to classify the image. We considered four types of land cover for image classification, man-made objects, bare-hill, vegetation and water. Through SMA, we quantify the areal fraction of these four type components at subpixel scales and interpret the fraction of individual component (end-member) as surrogates for the fuzzy membership function value.
SMA classification result of land cover of Hong Kong. (End-member fraction of man-made, bare-hill, vegetation, water)
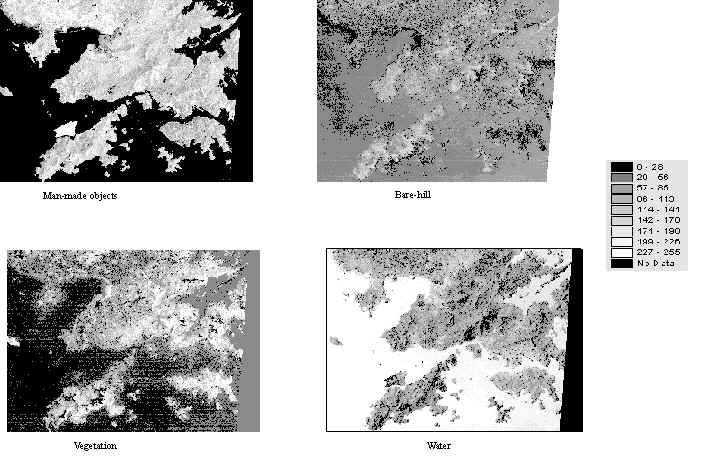
Based upon the fuzzy classification results and fuzzy object models, the core of FC-objects and FC-objects are formed, which are shown below.

Nowadays, huge volume of geo-referenced data has been available to geographers and other scientists. This data-rich environment is considerably different from the data-poor environment when Geographic Information System (GIS) originated. Furthermore, simple query and retrieval function of GIS can not satisfied with need of geographers and other scientists. On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) occurs to facilitate the decision-maker to gain insight from large treasury of data, instead of drowning in the sea of unmeaning data. We believe that OLAP and GIS should be integrated so that we can make the most of the geographic data.

OLAP is widely employed in private business to analyze its own data. Quite different from this, much of geo-referenced data is obtained by government department. For this reason, public can assess this geo-referenced data almost free although the data is collected with very high cost. Therefore, web technology should also be integrated into this OLAP system in order to make as many scientists as possible to analyze this valuable data intensively.
Now we are constucting a prototype system targeting on facilitating users' access to GIS OLAP function online.
Please contact Mr. SHAN Yin for further informatin.
This collection of visualized economic indicators intends to provide readers with visualized (Geographic Information System, GIS) inspections of the investment environments of the two globalized delta economies in China - Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and Pearl River Delta (PRD) at both the municipality (Shi) and county/city/district levels. Following the theoretical model developed by the authors, four major components of an investment environment with 28 indicators were constructed using published official secondary data.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne infection the incidence of which varies with the environment and climate. Knowingly, the reported incidence of dengue is an insensitive indicator of infection risk in a locality. Ovitrap Index has been in use in many countries. This is a measurement of mosquito eggs in specified geographic location, which in turn reflects the distribution of Aedine mosquitoes, the vector for dengue. Using GIS application, an alert system was created from a synthesis of geospatial data on Ovitrap indices in Hong Kong. The inter-relationship between Ovitrap indices and temperature was made. This forms the rationale for the generation of weighted overlays to define risk levels. The weighting could be controlled to set the sensitivity of the alert system. This system can be operated at two levels, one for the general public to assist the evaluation of dengue risk in the community, and the other for professionals and academia for supporting technical analysis. The alert system offers one objective means to define risk of dengue in a society, which would not be affected by the incidence of the infection itself.
Please click here to download the paper.
This project deals with the region of Ming Songjiangfu and Ming Jiading county in the Lower Yangzi delta, roughly equivalent to the modern Shanghai Municipality, in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries. This region was the major cotton textile production area of late imperial China.
There are three major objectives for this project:
In sum, this is a multidisciplinary study combining socioeconomic history, local history, GIS, regional analysis, and new institutional economics with a view to generating new understanding of and research strategies towards China’s economic development past and present.
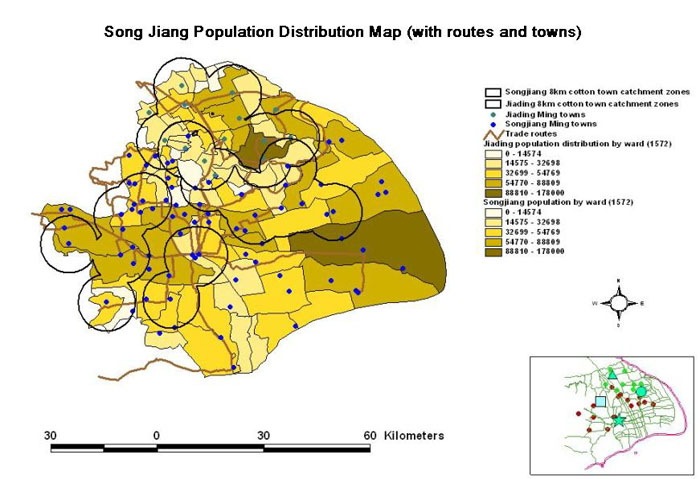
For details, please click this link:http://www.iseis.cuhk.edu.hk/songjiang



Geographic Real Estate Information System is a GIS based Investment Environment information system can be used to enhanced the communication between investors and regional developers or local goveronment.

When there is an incoming call, the computer will automatically pops up the location of the caller by digital maps, also provide spatial information of the caller. Real-time Identification of the caller's location and geographic analysis for emergency.
There are three modules in the system:
For the last five years, the Department of Architecture of the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), in coolaboration with the Ministry of Construction of China (MOC) has several research projects in the area of Low Cost Urban Housing in China.
The issues of livability energy efficiency, environment quality, building materials and contruction have been the major focus. One project of particular interest to the MOC has been the development of a pilot design for low cost urban housing that makes use of the latest technology available. Taking into account variations in climate, local customs and indigenous materials, the prototype design can be replicated and modified throughout China. The intention is to design living spaces based on application of modern technology that will improve the quality of residential life for low income families.

With the cooperation of the Department of Geography, we intend to apply GIS systems to information management planning for the Urban China Pilot Housing project.With the cooperation of the Department of Geography, we intend to apply GIS systems to information management planning for the Urban China Pilot Housing project.
The application of GIS represents an important cross disciplinary approach towards achieving a higher efficiency and better planning for urban in China. In areas of siting, housing typologies, density planning, and other related databased GIS can be immensely important. This information will be disseminated through the Internet and will serve all concerned with developing new ideas for improving the quality of China Housing.
Geographic information technology has been increasingly recognized and widely applied in certain fields in China since the beginning of 1990s. Following several top political and scientific advocators, more and more researchers, government officers, information engineers and end users are devoting to the domestic GIS industrial development and national geographic information strategy. However, their visions, opinions, suggestions or recommendations on GIS development in China are rather diversified and contradictions. In such academic context, this research introduces innovation diffusion theory to the study of GIS diffusion in China, and attempts to investigate general characteristics of GIS diffusion through theoretical model-building and empirical analyses.
Based on literature review of innovation diffusion theory, GIS diffusion studies and GIS technological development, a general model of GIS diffusion at national level is formulated as dynamic interactions between GIS echnology, processes of adopting GIS within an organization, and its external environments. GIS are organized activities by which people measure and represent geographic phenomena and then transform these representations into other forms of knowledge while interacting with organizational and social structures.
The processes of GIS diffusion within an organization can be generalized as dynamic interactions between knowledge accumulation, investment decision-making, system implementation, system application, and assessment of GIS utilization. nowledge learning and decision-making are two determining factors within the full cycle of GIS diffusion. National GIS diffusion environment mainly concerns market conditions, knowledge bases, institutional settings, and socioeconomic and cultural contexts. Market environment is the most undamental factor influencing GIS diffusion for a long term and other factors effecting GIS by directly or indirectly effecting market mechanism.
On the other hand, multiple data sources, resulting from questionnaire survey, case study, individual interview, Internet information, academic database and commercial database, are empirically analyzed to investigate the organizational and institutional characteristics of GIS development, application and diffusion in China. It is concluded that:
This GIS diffusion research has rich implications for GIS development, in terms of improvement of GIS implementation in an organization and improvement of external environment of GIS diffusion. Firstly, it help to understand and explain the GIS diffusion process within an organization, and therefore contribute to the organizational effectiveness of knowledge accumulation, investment decision making, system implementation, and management assessment of adopting GIS technology. Secondly, the environmental research potentially provides fundamental, but essential, factors that facilitate or prohibit GIS applications. The findings from such research are critical for government policy making on geographic information dissemination and national strategic GIS development.
Please contact Mr. KONG Yunfeng for further information.

SQL/SDA is a query language particularly designed for complicated multi-step spatial data analysis. It has two distinct features:
Please click here to download the project details.
A tool called GeoVR has been designed and developed under a client/server architecture to enable the interactive creation of 3D scene and Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) model from 2D spatial data by integrating Internet Geographical Information System (GIS) and HTML programming.

The client front-end of this tool provides a HTML form to set properties for building 3D scenes, while the server back-end supported by off-the-shelf software: ArcView Internet Map Server and ArcView 3D analyst through Avenue programming, processes the parameters and generates a 3D scene. This 3D scene is then transformed into a VRML model, which, together with its legend, is sent back to the VRML-enabled WWW browser for display and navigation.

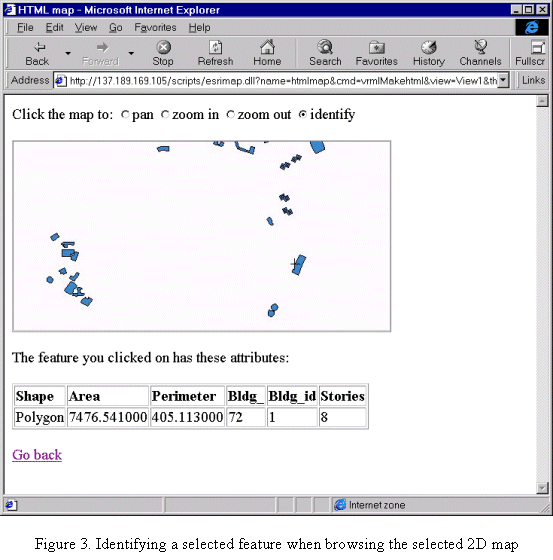
It is demonstrated that this tool, not only automates the conversion of the conventional 2D GIS data into VRML, but also adapts the current GIS 3D capabilities to the increasingly popular Web environment. The development of such a tool offers new opportunities for users to build applications that benefit from virtual reality presentation based upon the existing GIS spatial databases.


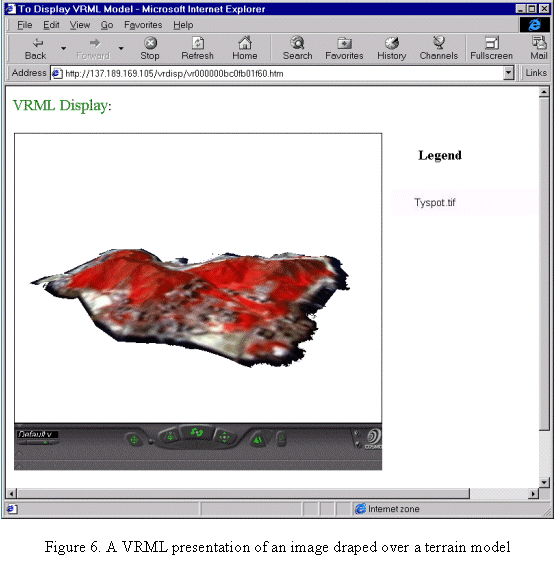

Geo-3DVision is a three-dimensional geo-referenced visualization system that can convert ditigal elevation model, remotely sensed images, landuse data, transportation spatial distribution, etc. into three-dimensional images, and can implement data query, cross-section analysis, computation of slope, aspect, and volume cut-fill, simulation of geo-referenced spatiao-temperoal model computing, etc. based on three-dimensional images.