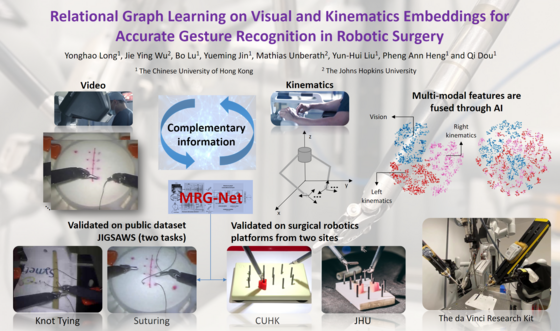
Relational Graph Learning on Visual and Kinematics Embeddings for Accurate Gesture Recognition in Robotic Surgery
Existing surgical robots often work in a remote control mode in which a surgeon tele-controls the robots with full attention. It is widely considered that such remote-controlled robots will be replaced by next-generation ones that will assist surgeons with high-level intelligence, and/or automatically perform particular steps of surgical procedures. The development of such intelligent surgical robots presents several big scientific challenges including (1) how to efficiently and reliably sense surgical objects/fields; (2) how to automatically carry out pre-operative (pre-op) surgical planning and navigate the robots in the highly dynamic and individual-dependent environment; (3) how to control the actions of surgical robots safely and accurately; and (4) how to equip surgical robots with high-level intelligence, e.g., the abilities of situation awareness and reasoning.
By combining the expertise and experiences in different areas, we aim to develop innovative solutions to those challenges, which include (1) novel systems and algorithms for real-time sensing of 3D geometry, force, and biomechanical properties of surgical objects; (2) data-driven surgical planning and navigation by using the huge image data of robotic surgery at the Prince of Wales Hospital (PWH) and Intuitive Surgical Inc.; (3) visually servoed controllers for robots interacting with soft tissues; and (4) robotic surgery intelligence based on deep learning. The technologies will be integrated into a prototype of image-guided surgical robots that is able to automatically assist surgeons and/or perform a single surgical step or several connected steps of surgical procedures. We will use the total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) as the example to validate the system by ex-vivo experiments, and if approved, by clinical trials and pilot applications.

