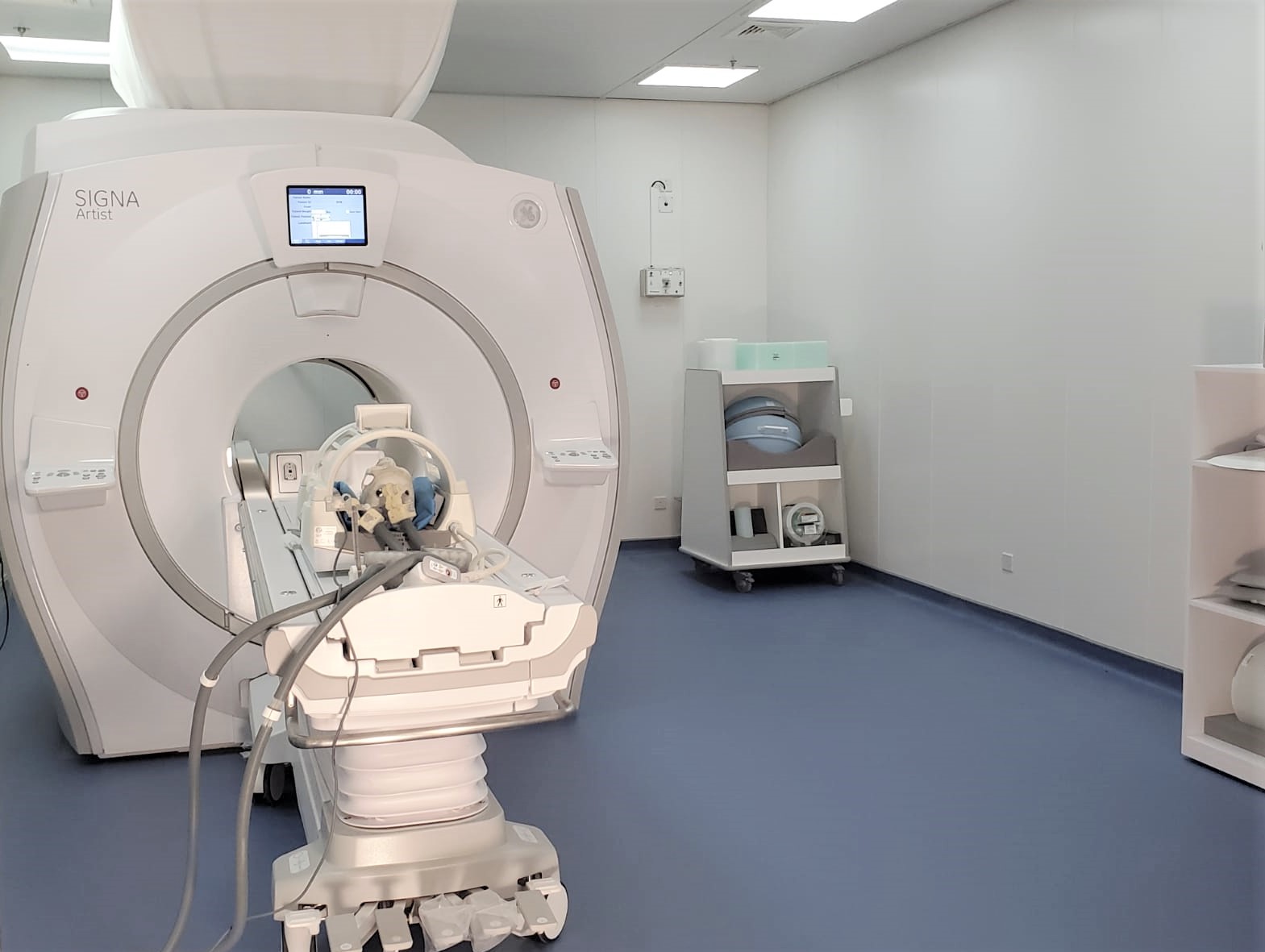
Intra-operative MRI-guided robot for bilateral stereotactic neurosurgery
Advanced surgical robotics has attracted significant research interest in supporting image guidance, even magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for effective navigation of surgical instruments, taking advantage of the high soft-tissue contrast and zero ionizing radiation. Precise, real-time temperature monitoring can also be achieved by intra-operative (intra-op) MRI to enable monitoring of ablation and heat diffusion to adjacent tissue. In situ effective guidance of access routes to the target anatomy, rendered based on intra-op MR image data, can enable a distinct awareness of the position of the robotic instrument tip relative to the target anatomy in various types of minimally invasive interventions.
Therefore, these proposed MRI-guided robots will rely on real-time processing the co-registration of the surgical plan with the imaging data captured during the intervention, as well as real-time localization of the instrument relative to the anatomy of surgical interest. The proposed robot systems would comprise three major technical features, namely 1) Compact design for accommodation of robot within the MRI bore and even the body/head coil; 2) Magnetic resonance MR-compatible actuation that could remotely-operate the robot in sufficient degrees-of-freedom (DoFs); and 3) MR-based tracking system localizing the surgical instruments relative the MR image coordinates. We will also validate the clinical potential of enhanced surgical safety by imposing high-fidelity imaging/sensing feedback on remotely-operated robotic instruments even under large-scale and rapid tissue deformations in soft tissue surgeries. The ultimate research objective is to enable the operator to perform safe, precise and effective control of robotics instruments with the aid of pre- and intra-op MRI models. The present work will be timely to bridge the current technical gap between MRI and surgical robotic control.

