Cong Zhang1,2, Hongsheng Li2, Xiaogang Wang2, and Xiaokang Yang1
1Institute of Image Communication and Network Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2Department of Informaiton Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
[PDF]
[Extended Abstract]
[Poster]
[Dataset]
Introduction
Counting crowd pedestrians in videos draws a lot of attention because of its intense demands in video surveillance,and it is especially important for metropolis security. In this paper, we propose a framework for cross-scene crowd counting. No extra annotations are needed for a new target scene. Our goal is to learn a mapping from images to crowd counts, and then to use the mapping in unseen target scenes for cross-scene crowd counting. To achieve this goal, we need to overcome the following challenges. 1) Develop effective features to describe crowd. Previous works used general hand-crafted features, which have low representation capability for crowd. New descriptors specially designed or learned for crowd scenes are needed. 2) Different scenes have different perspective distortions, crowd distributions and lighting conditions. Without additional training data, the model trained in one specific scene has difficulty being used for other scenes. 3) For most recent works, foreground segmentation is indispensable for crowd counting. But crowd segmentation is a challenging problem
and can not be accurately obtained in most crowded scenes. The scene may also have stationary crowd without movement. 4) Existing crowd counting datasets are not sufficient to support and evaluate cross-scene counting research.

Considering these challenges, we propose a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based framework for cross-scene crowd counting. After a CNN is trained with a fixed dataset, a data-driven method is introduced to fine-tune (adapt) the learned CNN to an unseen target scene, where training samples similar to the target scene are retrieved from the training scenes for fine-tuning. Our cross-scene crowd density estimation and counting framework has following advantages:
- Our CNN model is trained for crowd scenes by a switchable learning process with two learning objectives, crowd density maps and crowd counts. The two different but related objectives can alternatively assist each other to obtain better local optima. Our CNN model learns crowd specific features, which are more effective and robust than handcrafted features.
- The target scenes require no extra labels in our framework for cross-scene counting. The pre-trained CNN model is fine-tuned for each target scene to overcome the domain
gap between different scenes. The fine-tuned model is specifically adapted to the new target scene.
- The framework does not rely on foreground segmentation results because only appearance information is considered in our method. No matter whether the crowd is moving or not, the crowd texture would be captured by the CNN model and can obtain a reasonable counting result.
- We also introduce a new dataset for evaluating cross-scene crowd counting methods. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest dataset for evaluating crowd counting
algorithms.
WorldExpo’10 Crowd Counting Dataset
We introduce a new large-scale cross-scene crowd counting dataset. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest dataset focusing on cross-scene counting. It includes 1132 annotated video sequences captured by 108 surveillance cameras, all from Shanghai 2010 WorldExpo. Since most of the cameras have disjoint bird views, they cover a large variety of scenes.
Our dataset is splitted into two parts. 1,127 one-minute long video sequences out of 103 scenes are treated as training and validation sets. There are 3 labeled frames in each training video and the interval between two labeled frames is 15 seconds. Some samples are shown as below:

The test set has 5 one-hour long video sequences from 5 different scenes. There are 120 labeled frames in each test scene and the interval between two labeled frames is 30 seconds. Some samples are shown as below:
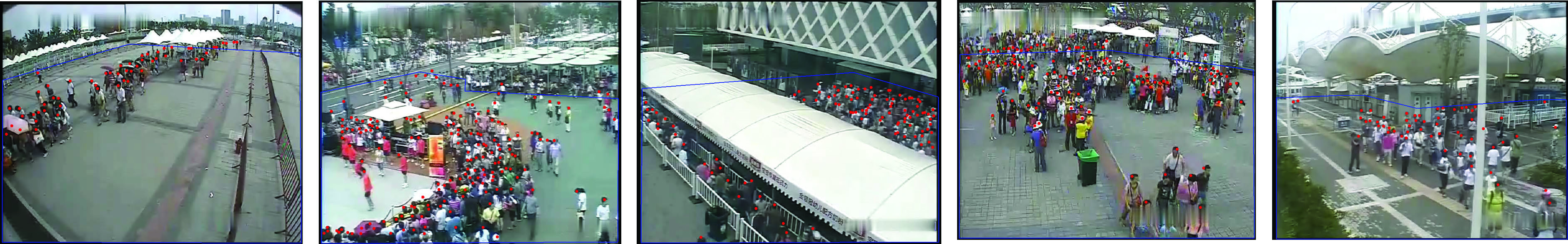
Description.
- The training set does not consist of any scene in the test set.
- The region within the blue polygons are the regions of interest (ROI) and positions of pedestrian heads are labeled with red dots.
- The perspective map is provided for each scene
- The dataset is available. This paper is in cooperation with Shanghai Jiao Tong University. SJTU has the copyright of the dataset. So please email Prof. Xie (xierong@sjtu.edu.cn) with your name and affiliation to get the download link. It's better to use your official email address.
- These data can only be used for academic research purposes.
Reference and Acknowledgments
Cong Zhang, Hongsheng Li, Xiaogang Wang, and Xiaokang Yang. "Cross-scene Crowd Counting via Deep Convolutional Neural Networks". in Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2015.
This work is partially supported by NSFC (No.
61025005, 61129001, 61221001, 61301269), STCSM
(No. 14XD1402100, 13511504501), 111 Program
(No. B07022), Sichuan High Tech R&D Program
(No. 2014GZX0009), General Research Fund sponsored
by the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong
(No. CUHK419412, CUHK417011, CUHK14206114,
CUHK14207814), Hong Kong Innovation and Technology
Support Programme (No. ITS/221/13FP) and Shenzhen Basic
Research Program (No. JCYJ20130402113127496).
Contact Me
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact me (zhangcong0929@gmail.com).
Last
update: June 5, 2015


