CUHK study sheds light on novel mechanism and treatment of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients
A recent study conducted by the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) has uncovered a SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid (N) protein that can induce acute kidney injury, which is common in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Using mice models, the CU Medicine research team proved that the viral N protein is pathogenic in acute kidney injury and can induce the injury directly by interacting with a transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) signalling molecule, Smad3, which is essential in causing tubular epithelial cell death.
Further experiments found that using Smad3 gene knockout technique or targeting the Smad3 signalling molecule with a pharmacological inhibitor can inhibit acute kidney injury specifically induced by SARS-CoV-2 N protein, suggesting a novel and specific therapy for COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury. These results have been peer reviewed and published in the international journal Advanced Science.
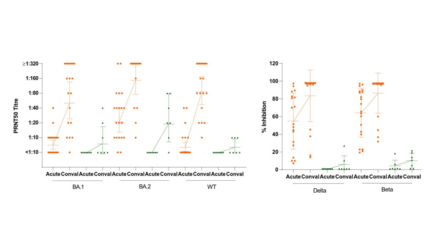
Over 40% of COVID-19 patients in ICU develop acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury is common in critically ill COVID-19 patients, characterised by elevated serum levels of creatinine, tubular necrosis and renal inflammation. The incidence of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients is closely related to the severity of the infection, as well as the underlying stress and disease conditions. Based on the published data, among critically ill COVID-19 patients hospitalised in the intensive care unit (ICU), more than 40% develop acute kidney injury with a high mortality rate. There are also studies showing that acute kidney injury is the second highest complication developed in critically ill COVID-19 patients after acute respiratory failure.
It is well understood that the S protein contained by SARS-CoV-2 can function to mediate the virus entry into the host cells. However, the mechanism by which the virus induces cell death in acute kidney injury was previously unknown.
Dr. Wen Biao WANG and Dr.Junzhe CHEN of the Department of Medicine and Therapeutics at CU Medicine are the co-first authors of the study. Based on their research, the kidney is one of the major target organs of COVID-19 but the current treatment for acute kidney injury is unspecific and ineffective. Therefore, identifying the mechanism specifically related to a SARS-CoV-2 protein that can induce cell death in acute kidney injury is urgently needed and is the first step towards the development of novel therapy.
SARS-CoV-2 N protein is proved to be pathogenic and can induce acute kidney injury
Using mice models, the research team discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 N protein is pathogenic and can induce acute kidney injury by causing tubular necrosis and elevated serum levels of creatinine. Under ischemic stress condition, the N protein can even cause more severe acute kidney injury. These findings matched the clinical observations that acute kidney injury is less severe in general patients with COVID-19 infection but becomes worse in those with ischemic and inflammatory stress conditions.
In addition, the team found that the SARS-CoV-2 N protein directly induces acute kidney injury by interacting with a signalling molecule, Smad3, to activate the cell death pathway. The activation of TGF-beta/Smad3 signalling can then cause tubular epithelial cell death in the kidney. Most importantly, the team proved that experimentally genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of Smad3 can prevent SARS-CoV-2 N protein-induced cell death as well as acute kidney injury. So, targeting inhibition of Smad3 may be a novel and specific therapy for COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury.
Professor Hui Yao LAN, leader of the research team and Choh-Ming Li Research Professor of Biomedical Sciences from the Department of Medicine and Therapeutics at CU Medicine, concluded, “My team has previously found that TGF-beta/Smad3 signalling is a key pathway leading to tissue fibrosis. Based on our latest experimental findings, it is suggested that SARS-CoV-2 N protein can interact with Smad3 to cause acute kidney injury and also, possibly, progressive organ fibrosis such as lung fibrosis in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Therefore, targeting Smad3 may not only inhibit acute kidney injury but also be a novel therapeutic strategy for COVID-19-related organ fibrosis. This gives us the hope of finding a new way to reduce the severity of the illnesses related to COVID-19.”
This study was supported by the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (14101121), the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao-Joint Labs Programme on Immunological and Genetic Kidney Diseases from Guangdong Science and Technology (2019B121205005), Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine (CARE program), the Hong Kong Scholars Programme (XJ2019052), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81902053). Details of the study: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202103248.