We spend one third of our time in bed. Why do we spend so much time sleeping? Why is sleep so important?
Sleep, just like diet and exercise, plays a vital role in good health and general well-being. After a long day work and study, sleep helps to “recharge” your body, protect your mental and physical health and prepare you with a good condition to continue working and studying the next day.
Sleep is not an inactive state. Indeed, lots physiological processes are happening during sleep. While you are sleeping, your brain is forming new pathways that helps your learning and memory, your body is repairing and healing, regulating various hormones.
In addition, the growth hormone secreted during sleep is three times more than that when you are awake, especially during deep sleep. So, if you want to be taller, you should cherish your sleep time!
Sleep, just like diet and exercise, plays a vital role in good health and general well-being. After a long day work and study, sleep helps to “recharge” your body, protect your mental and physical health and prepare you with a good condition to continue working and studying the next day.
Sleep is not an inactive state. Indeed, lots physiological processes are happening during sleep. While you are sleeping, your brain is forming new pathways that helps your learning and memory, your body is repairing and healing, regulating various hormones.
In addition, the growth hormone secreted during sleep is three times more than that when you are awake, especially during deep sleep. So, if you want to be taller, you should cherish your sleep time!
Sleep Science

Sleep Science

Sleep is often misunderstood as a passive and static process. In fact, when we fall asleep, our brain still maintain a certain degree of activity. Scientific research has proved that many important processes occur during sleep, and sleep has a significant impact on our physical and mental health.
By analyzing different brain waves during sleep, sleep can be divided into two main stages: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Non-REM sleep consists of three stages from stage 1 to stage 3, with stage 3 is deep sleep stage. During deep sleep, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and respiratory rate gradually decrease. Many physiological processes, which are beneficial to the human body, occur in this stage, such as secretion of growth hormone, recovery of energy, recovery and repair of the body, etc.
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep stage, also most commonly known as dreaming stage, accompanied with low muscle tone throughout the body. During this stage, heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature will increase, respiratory rate will become irregular, and dreaming often occur at this stage.
A night of sleep consists of alternating cycles of NREM and REM sleep, progress cyclically from stage 1 through REM then begin again with stage 1. In general, a complete sleep cycle last for 90 to 120 minutes, resulting in 4-5 cycles per night.
By analyzing different brain waves during sleep, sleep can be divided into two main stages: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Non-REM sleep consists of three stages from stage 1 to stage 3, with stage 3 is deep sleep stage. During deep sleep, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and respiratory rate gradually decrease. Many physiological processes, which are beneficial to the human body, occur in this stage, such as secretion of growth hormone, recovery of energy, recovery and repair of the body, etc.
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep stage, also most commonly known as dreaming stage, accompanied with low muscle tone throughout the body. During this stage, heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature will increase, respiratory rate will become irregular, and dreaming often occur at this stage.
A night of sleep consists of alternating cycles of NREM and REM sleep, progress cyclically from stage 1 through REM then begin again with stage 1. In general, a complete sleep cycle last for 90 to 120 minutes, resulting in 4-5 cycles per night.
Factors Affect Your Sleep

Factors Affect Your Sleep

Internal factors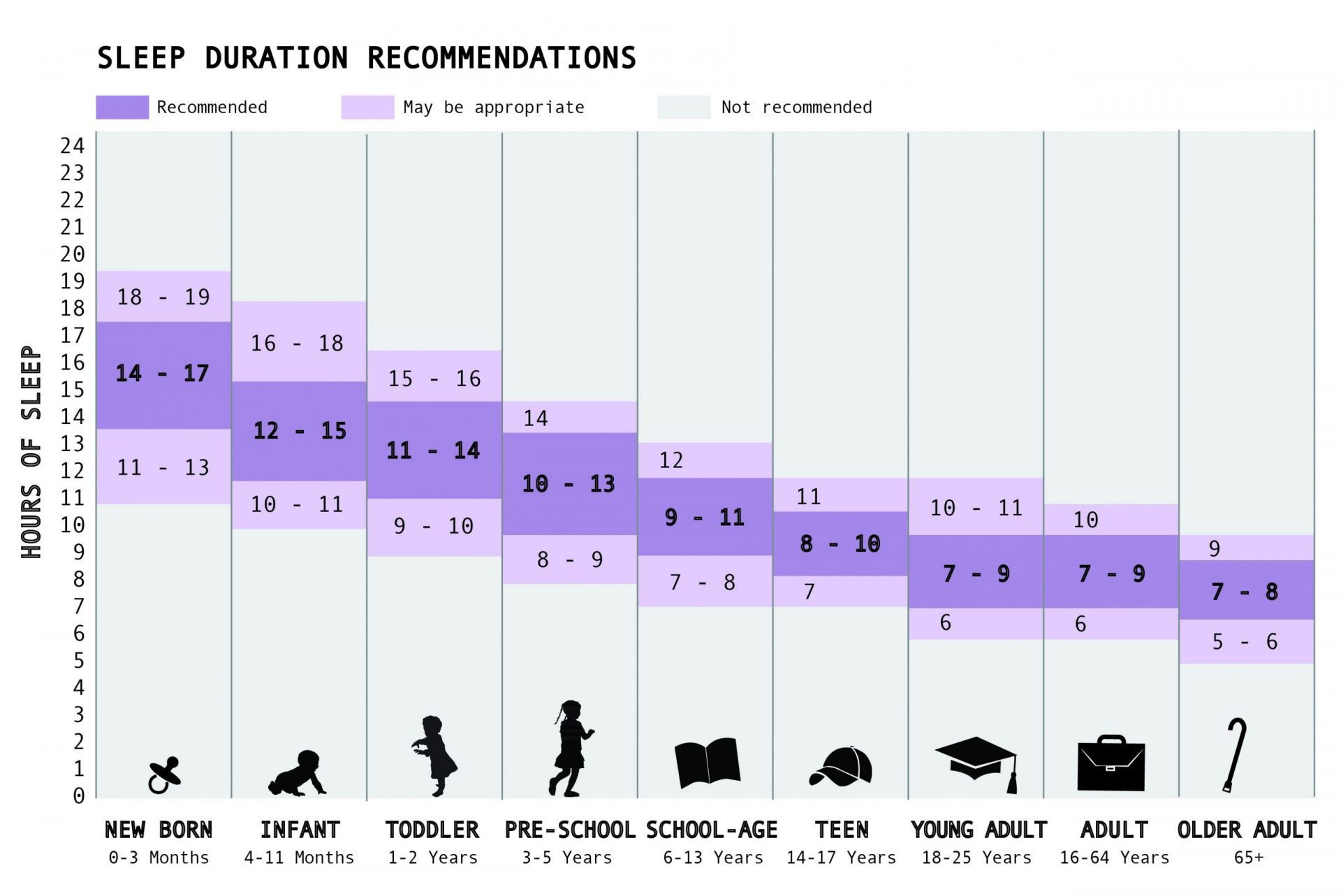
There are several internal factors directly control our sleep-wake cycle:
External factorsThere are many external factors that may affect our sleep-wake pattern, for example:
Besides, do you know other factors that affect our sleep?
Recall how many hours you sleep last night, then take a look at the chart below. 
How to tell if you are getting enough sleep?

How to tell if you are getting enough sleep?

In fact, the amount of sleep needed is different for everyone. For some people, they need to sleep a lot. Some only need a few hours. The difference lies in our genes.
The easiest way to know if you are sleeping enough is to pay attention to whether you feel energetic or tired as you wake up. If you often feel tired or lack of energy during the day, it means that you are not getting enough sleep. So, have good night sleep tonight!
The easiest way to know if you are sleeping enough is to pay attention to whether you feel energetic or tired as you wake up. If you often feel tired or lack of energy during the day, it means that you are not getting enough sleep. So, have good night sleep tonight!
Healthy sleeping habit

Healthy sleeping habit

Insufficient sleep can have both short term and long-term effect on our body. Therefore, adequate sleep is necessary for our general well-being. To improve your sleep, you should develop good sleeping habits. Check if you have done the followings:
Regular sleep-wake pattern: maintain regular bedtime and wakeup time everyday, so as to develop a fixed schedule for your biological clock.
Establish a regular and relax bedtime routine: establish a regular and relaxing routine such as taking a warm bath or some snacks to notify your body it’s time for bed.
Pleasant sleep environment: Turn off the lights, and keep the bedroom dark, maintain a quiet and moderate temperature bedroom environment.
Use bed only for sleep and sex. Do not study or work on bed.
Avoid using light-emitting devices (e.g., computers, TVs and mobile phones, etc) 30 minutes before bed.
Do not eat too much or be starve yourself before bed.
Avoid vigorous activity 2 hours before bedtime.
Avoid caffeine, alcohol and smoking 4 to 6 hours before bedtime.
Do not worry about tomorrow’s exams or homework. A relaxing mind helps put you to sleep.
Still cannot fall asleep?
Do not force yourself to fall asleep. If you can’t sleep for over 30 minutes, it is advised to leave your bed, do some relaxing activity and go back to sleep when you feel sleepy.
Do something relaxing, for example, listen to soft music.
Recall some good memories to make yourself happy.
If your problem persist, you should consult the doctor.



