Joint CUHK-HKU study discovers efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines correlates with a probiotic bacterium, Bifidobacterium adolescentis

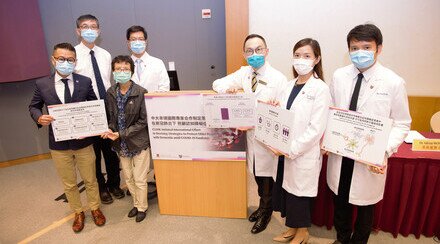
(From left) Dr. Hein TUN,Assistant Professor of the School of Public Health at HKUMed; Professor Siew Chien NG, Associate Director of the Centre for Gut Microbiota Research, CU Medicine; Professor Francis CHAN, Dean and Director of the Centre for Gut Microbiota Research, CU Medicine; and Professor Lin ZHANG, Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, CU Medicine.
The Centre for Gut Microbiota Research of the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) is among the first in the world to discover that germs in our gut (gut microbiota) modulate our immunity and disease severity in COVID-19. In a collaborative research project between CU Medicine and the LKS Faculty of Medicine at The University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), the research team showed that the efficacy of SinoVac and BioNTech correlated with a unique bacterium, Bifidobacterium adolescentis. They found that people who lacked Bifidobacterium adolescentis in their gut had a suboptimal antibody response to SinoVac. Among BioNTech recipients, those who lacked two types of bacteria including Bifidobacterium adolescentis also had lower antibody response. These novel findings imply that Bifidobacterium adolescentis can serve as a potential therapeutic option to enhance efficacy of SinoVac and BioNTech.
The first human study to provide evidence that gut microbiota modulates vaccine response
The efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines declines with time. Dr. Hein TUN,Assistant Professor of the School of Public Health at HKUMed said, “There are two possible mechanisms how our gut microbiota can boost antibody response to vaccines: first, some components of gut bacteria such as flagellin serve as natural adjuvant to enhance antibody production; and secondly, gut microbiota produces metabolites such as short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that can enhance immune cell metabolism to support energy demands for antibody production.”
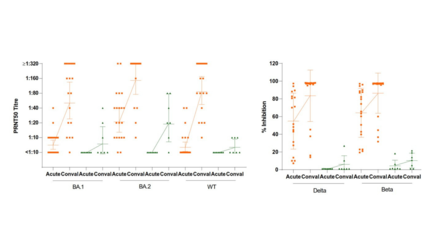
Between April and August 2021, the research team recruited 138 residents aged between 18 and 67. All participants provided blood and stool samples before vaccination and one month after the second dose. The research team measured their antibody level in relation to their gut bacterial composition.
People lacking Bifidobacterium adolescentis showed poor antibody response to COVID-19 vaccines
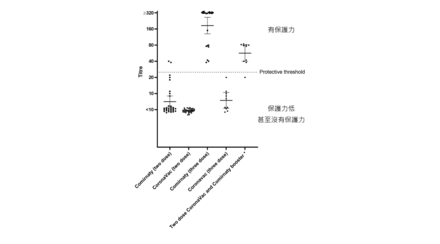
The results showed that over half of the people who received SinoVac had a suboptimal antibody response. There was a close correlation between low antibody response and lack of a unique bacterium in our gut called Bifidobacterium adolescentis. Among BioNTech recipients, those who lacked two bacteria including Bifidobacterium adolescentis also showed lower antibody response.
Bifidobacteria belong to a family of probiotic bacteria in our gut. Unlike other members of bifidobacteria, the team found that only Bifidobacterium adolescentis was associated with antibody response to SinoVac. Bifidobacterium adolescentis lives in our gut since birth and its abundance declines rapidly with age, modern diet, stress, and the use of antibiotics. Diet alone fails to restore this precious bacterium once it is lost. Many health products contain Bifidobacteria but very few have Bifidobacterium adolescentis. In an earlier CUHK study of over 2,000 Hong Kong citizens, researchers found that Bifidobacterium adolescentis was either very low or absent in 85% of otherwise healthy Hong Kong people.
Professor Siew Chien NG, Associate Director of the Centre for Gut Microbiota Research at CU Medicine, explained, “This is the first proof in humans that Bifidobacterium adolescentis plays an important role in modulating the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. The inactivated vaccine (SinoVac) is known to have fewer side effects but suffers from relatively lower antibody response. Our study offers a potential solution to enhance the efficacy of SinoVac.”
Professor Francis CHAN, Dean and Director of the Centre for Gut Microbiota Research at CU Medicine, said, “This new discovery is consistent with our earlier clinical findings[i] that a microbiota-based regimen developed by CUHK, which contains Bifidobacterium adolescentis, led to enhanced antibody response among COVID-19 patients. Our study provides evidence that Bifidobacterium adolescentis is a key to modulate antibody response of COVID-19 vaccines. We believe this discovery offers a novel approach to optimize vaccine efficacy and safety through modulation of the gut microbiota.”
This study was funded by the Health and Medical Research Fund of the Food and Health Bureau, Enhanced start-up research grant of HKU, and the National Research Foundation of Korea grant.
[i] 40% of Hong Kong People Show Gut Dysbiosis Comparable to that of COVID-19 Patients CUHK Microbiome Immunity Formula Hastens Recovery of COVID-19 Patients and Offers Hope to Boost Immunity (Details: https://bit.ly/3fmo10D)