CU Medicine study shows a higher prevalence of dry eye disease among post-COVID-19 patients
Some COVID-19 patients develop various and persistent symptoms weeks and months after completely recovering from the infection. Investigators from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences of The Chinese University of Hong Kong’s (CUHK) Faculty of Medicine (CU Medicine) have found that one in five post-COVID patients have at least one recent-onset symptom related to dry eye disease (DED) such as blurred vision, itching, pain, or burning. In addition, the study showed that the risk of DED is linked to the severity of COVID infection. The findings have recently been published in the international journal Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (the official journal of The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Ophthalmologists).
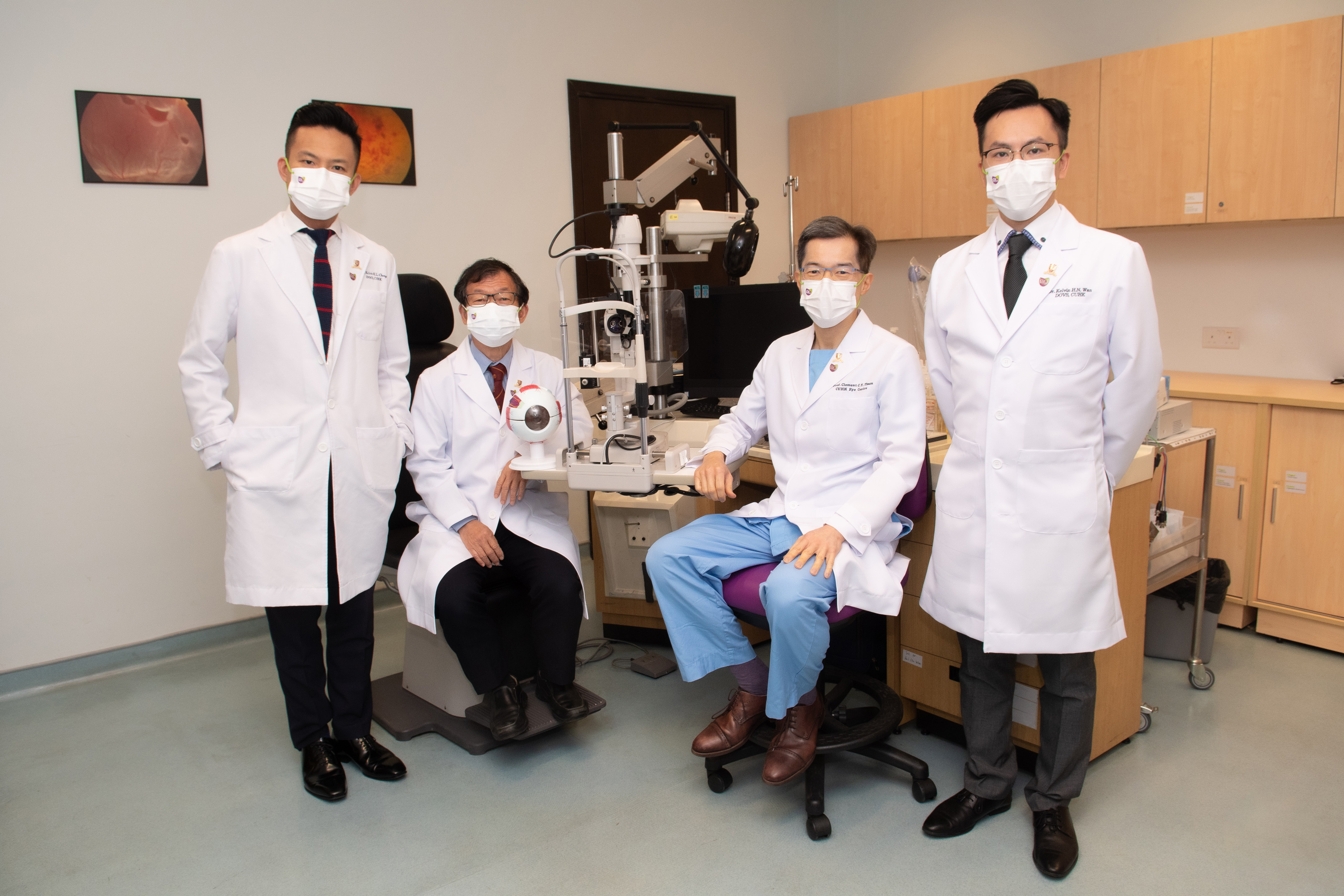

Investigators from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences of CU Medicine have found that 1 in 5 post-COVID patients have at least one recent-onset symptom related to the dry eye disease (DED). In addition, the study showed that the risk of DED is linked to the severity of COVID infection. (From left) Dr. Kelvin KL CHONG, principal investigator of the study and Associate Professor; Professor Calvin CP PANG, S.H. Ho Research Professor of Visual Sciences; Professor Clement CY THAM, Department Chairman and S.H. Ho Professor of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences; and Dr. Kelvin HN WAN, the lead author of the study and Assistant Professor from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, CU Medicine.
Symptoms of DED include grittiness, pain, blurred vision and more
Affecting tens of millions of individuals globally, DED is a major reason for patients seeking eye care. In Hong Kong, the estimated prevalence is 30%. DED is characterised by an unstable and a more concentrated (termed “hyperosmolar”) tear film, leading to increased inflammation and damage to ocular surface structures and nerves. Symptoms of DED include eye grittiness, pain or soreness, burning, watering, light sensitivity, and blurred vision. DED carries significant socioeconomic implications, including medical costs and disruption of work.
Professor Clement CY THAM, Chairman and S.H. Ho Professor of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, CU Medicine said, “DED can significantly impair daily social and physical functions, such as reading, uses of digital devices and driving. Workplace productivity is affected by the increased time and cost spent on treatment and the avoidance of specific environments in the workplace that aggravate dry eye symptoms.”
Professor Calvin CP PANG, S.H. Ho Research Professor of Visual Sciences, CU Medicine has been studying the ocular effects of COVID on adults and children. “COVID can have direct clinical effects on people’s eyes. This also affects people indirectly through disruption of normal working and living activities.”
Post-COVID patients have a greater risk of dry-eye-related ocular surface manifestations
The CUHK research team evaluated 228 post-COVID patients one to three months after their diagnoses, who took place between February and December 2020, and 109 healthy age-matched participants. All participants received comprehensive eye examinations, and anyone with any pre-existing ocular surface conditions, a previous history of refractive surgery, ophthalmic surgery or ocular trauma, who had used contact lenses within the past three months or who were using eye medication of any kind, were not included in the study.
During the study, all participants underwent comprehensive eye examinations including evaluation for meibomian gland dysfunction, the most common cause of DED, and corneal fluorescein staining, an indicator of DED severity. It was found that post-COVID patients had a higher prevalence of dry-eye-related ocular surface manifestation than healthy individuals.
Comparison of the dry-eye-related ocular surface manifestation between post-COVID patients and healthy individuals:
| Post-COVID patients | Healthy individuals |
|---|---|---|
Meibomian gland dysfunction staging# | 1.14±0.67** | 0.92±0.68 |
Proportion of eyes with any positive corneal fluorescein staining | 48.9%* | 38.6% |
Corneal fluorescein staining score# | 0.60±0.69* | 0.49±0.68 |
Statistical significance *p<0.05, **p<0.005 Remarks: # Graded on a 4-point scale (0=absent, 1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe) | ||

Meibomian gland dysfunction is the most common cause of DED. The malfunction of tiny oil glands which line the margin of the eyelids will result in tear film instability. Study data shows post-COVID patients who appear with DED symptoms have mild Meibomian gland dysfunction score.

Dry eyes may lead to scarring of the front surface of the eye, appear like cracked skin. Corneal fluorescein staining can detect damage to the cornea.
With post-COVID patients who received any form of supplementary oxygen during hospitalisation, the tear break-up time (an indicator of tear evaporation, the average break-up time of a health person is usually over 10 seconds) was 1.6 seconds shorter, implying a higher likelihood of DED when compared to those not requiring oxygen during hospitalisation. One of the reasons for this is that the gas flow from oxygen delivery may increase the evaporation of the tear film.
Dr. Kelvin HN WAN, the lead author of the study and Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences of CU Medicine said, “We found that every one-point reduction in Ct-value (inversely correlated with the viral load) from the respiratory specimen collected at hospital admission increased the risk of having any dry-eye-related ocular surface symptoms during the first month after recovery by 10%. This finding suggests the risk of tear film instability after recovery from COVID is associated with the severity of the acute infection.”
The post-COVID patients were asked about their dry-eye-related ocular surface symptoms using a questionnaire at the time of ophthalmic assessment after discharge. Over 20% of post-COVID patients (21.5%) had developed at least one of these symptoms, most commonly blurred vision (9%), itching (6.1%), pain or burning sensation (4.8%), tearing or discharge (3.9%), and redness (3.1%).
Summary of the prevalence of recent-onset dry eye symptoms among post-COVID patients:
Dry eye symptoms | Percentages of post-COVID patients presenting related symptoms |
|---|---|
Blurring | 9.2% |
Itch | 6.1% |
Pain or burning sensation | 4.8% |
Tearing or discharge | 3.9% |
Redness | 3.1% |
Grittiness | 2.2% |
Light-sensitivity | 1.8% |
Lid swelling | 1.3% |
One or more than one related symptoms | 21.5% |
Dr. Kelvin KL CHONG, principal investigator of the study and Associate Professor, Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, CU Medicine said, “The outcome of our study is one additional strong reason why each one of us should complete our COVID-19 vaccination regime as soon as possible. A completed vaccination regime is currently the most important and effective measure one can take to significantly raise the Ct value, that is to lower the disease severity if infected, and decrease the chance of developing severe COVID-19 requiring supplementary oxygen. Vaccination remains the most effective measure in preventing post-COVID-19 eye symptoms and all other longer-term sequelae.”
The study was supported by the Health and Medical Research Fund, Hong Kong SAR, project number COVID190106.