What Is Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test in which a small amount of amniotic fluid is removed from the sac surrounding the fetus for testing. The sample of amniotic fluid (less than one ounce) is removed through a fine needle inserted into the uterus through the abdomen, under ultrasound guidance. The fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Different tests can be performed on a sample of amniotic fluid, depending on the genetic risk and indication for the test.
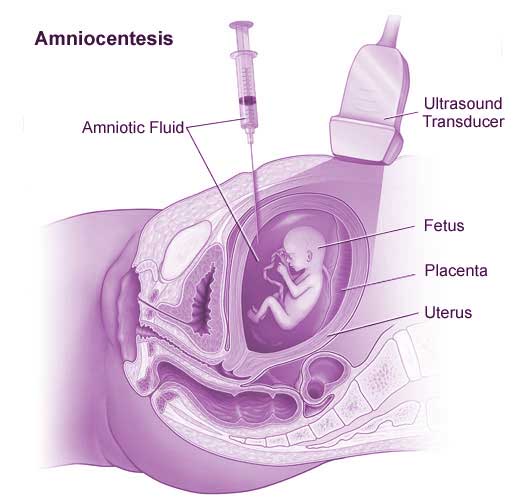
Why Is an Amniocentesis Performed?
Amniocentesis can be used to detect a number of conditions, such as:
- Down’s syndrome – a genetic condition that affects a person’s physical appearance and mental development
- spina bifida – a series of birth defects that affect the development of the spine and nervous system
- sickle cell anaemia – a genetic disorder that causes a person’s red blood cells to develop abnormally
Amniocentesis is usually carried out after week 16 of the pregnancy.
This is because the procedure is invasive (involves going into the body) and has a small risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.2%).
